| Name | Project | Type | Compare |
|---|---|---|---|
| Örebro-Vivalla | JUST PEPP | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Tiurberget, Kongsvinger | JUST PEPP | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Texel | JUST PEPP | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Hällefors, Sweden | JUST PEPP | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Cerdanyola del Valles, School of Engineering, Campus Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona | OPEN4CEC | PED Lab | Compare |
| Bucharest, The Bucharest University of Economic Studies (ASE) PED Lab | OPEN4CEC | PED Lab | Compare |
| Pamplona | OPEN4CEC | PED Lab | Compare |
| Trondheim, Svartlamon | OPEN4CEC | PED Lab | Compare |
| Savona, The University of Genova, Savona Campus | OPEN4CEC | PED Lab | Compare |
| Torres Vedras, Encosta de São Vicente | COPPER | PED Lab | Compare |
| Malmö, Stadium area (Stadionområdet) | PED StepWise | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Utrecht, Utrecht Science Park | PED StepWise | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Vienna, Kriegerheimstätten | PED StepWise | PED Relevant Case Study | Uncompare |
| Vienna, 16. District, Leben am Wilhelminenberg | HeatCOOP | PED Relevant Case Study | Uncompare |
| Vienna, Laxenburgerstraße AH | HeatCOOP | PED Lab | Compare |
| Tartu, Annelinn | V2G-QUESTS | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Utrecht, Kanaleneiland | V2G-QUESTS | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Aveiro, Aradas district | V2G-QUESTS | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Győr, Geothermal District Heating Project | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Drammen, Jacobs Borchs Gate | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Freiburg im Breisgau, Dietenbach | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Lecce, SmartEnCity | SmartEnCity – Towards Smart Zero CO2 Cities across Europe | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Trento, STARDUST | STARDUST – Holistic and Integrated Urban Model for Smart Cities | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Malmö, Klimatkontrakt Hyllie | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Kaiserslautern, EnStadt:Pfaff | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| Helsinki, mySMARTlife | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Firenze, Novoli-Cascine district on “le PIagge” buildings | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Bolzano, Sinfonia | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Zürich, Hunziker Areal | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Hammarby Sjöstad, Hammarby Sjöstad 2.0 | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Milano, Sharing Cities | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Mieres, District Heating Pozo Barredo | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Lund, Cityfied (demo Linero) | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Espoo, Smart Otaniemi | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| Vienna, Zukunftsquartier | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Trento, Santa Chiara Open Lab | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Paterna, Barrio La Pinada | PED Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| Bergen, Zero Village Bergen (ZVB) | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Võru, +CityxChange | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Trondheim, NTNU Campus within the Knowledge Axis | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Oslo, Furuset project | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Măgurele, Laser Valley – Land of Lights | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Elverum, Ydalir project | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Bodø, Airport, NyBy – Ny Flyplass (New City – New Airport) | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Bærum, Fornebu | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Carquefou, Fleuraye west | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Åland, Smart Energy | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Romania, Alba Iulia PED | ASCEND – Accelerate poSitive Clean ENergy Districts | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Romania, Alba Iulia PED | InterPED – INTERoperable cloud-based solution for cross-vector planning and management of Positive Energy Districts | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Munich, Harthof district | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Lublin | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Roubaix, MustBe0 – Résidence Philippe le Hardi – 125 Rue d’Oran | CULTURAL-E – Climate and cultural-based solutions for Plus Energy Buildings | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Bærum, Eiksveien 116 | CULTURAL-E – Climate and cultural-based solutions for Plus Energy Buildings | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Findhorn, the Park | InterPED – INTERoperable cloud-based solution for cross-vector planning and management of Positive Energy Districts | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Amsterdam, Buiksloterham PED | ATELIER – AmsTErdam BiLbao cItizen drivEn smaRt cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Schönbühel-Aggsbach, Schönbühel an der Donau | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Umeå, Ålidhem district | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Aalborg East | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| Ankara, Çamlık District | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Trenčín | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Luxembourg, Betzdorf | LEGOFIT – Adaptable technological solutions based on early design actions for the construction and renovation of Energy Positive Homes | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Vantaa, Aviapolis | NEUTRALPATH – Pathway towards Climate-Neutrality through low risky and fully replicable Positive Clean Energy Districts | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Vidin, Himik and Bononia | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Oslo, Verksbyen | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Case Study | Compare |
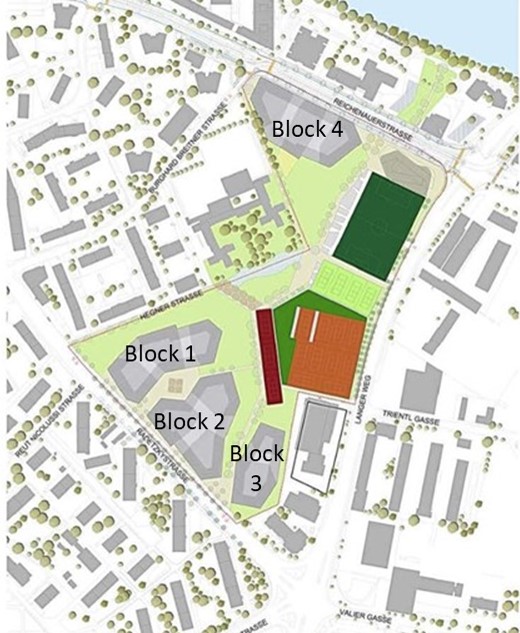
| Uden, Loopkantstraat | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Relevant Case Study | Uncompare |
| Zaragoza, Actur | NEUTRALPATH – Pathway towards Climate-Neutrality through low risky and fully replicable Positive Clean Energy Districts | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Aarhus, Brabrand | BIPED – Building Intelligent Positive Energy Districts | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Riga, Ķīpsala, RTU smart student city | ExPEDite – Enabling Positive Energy Districts through Digital Twins | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Izmir, District of Karşıyaka | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Istanbul, Ozyegin University Campus | LEGOFIT – Adaptable technological solutions based on early design actions for the construction and renovation of Energy Positive Homes | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Espoo, Kera | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study | |
| Borlänge, Rymdgatan’s Residential Portfolio | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Freiburg, Waldsee | PED urban – Development of methods and tools for accounting, planning and operation of climate-neutral district | PED Case Study | Compare |
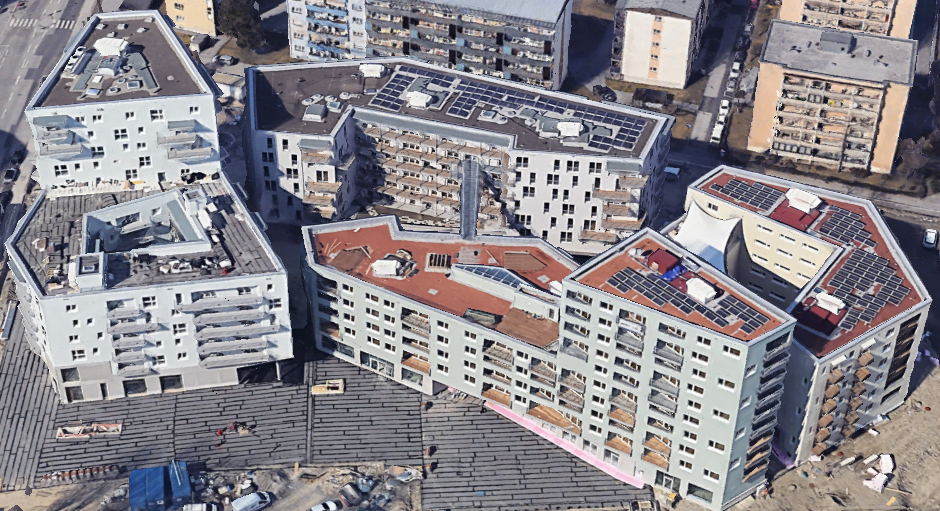
| Innsbruck, Campagne-Areal | PED Relevant Case Study | Uncompare | |
| Graz, Reininghausgründe | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Stor-Elvdal, Campus Evenstad | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Oulu, Kaukovainio | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Halmstad, Fyllinge | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
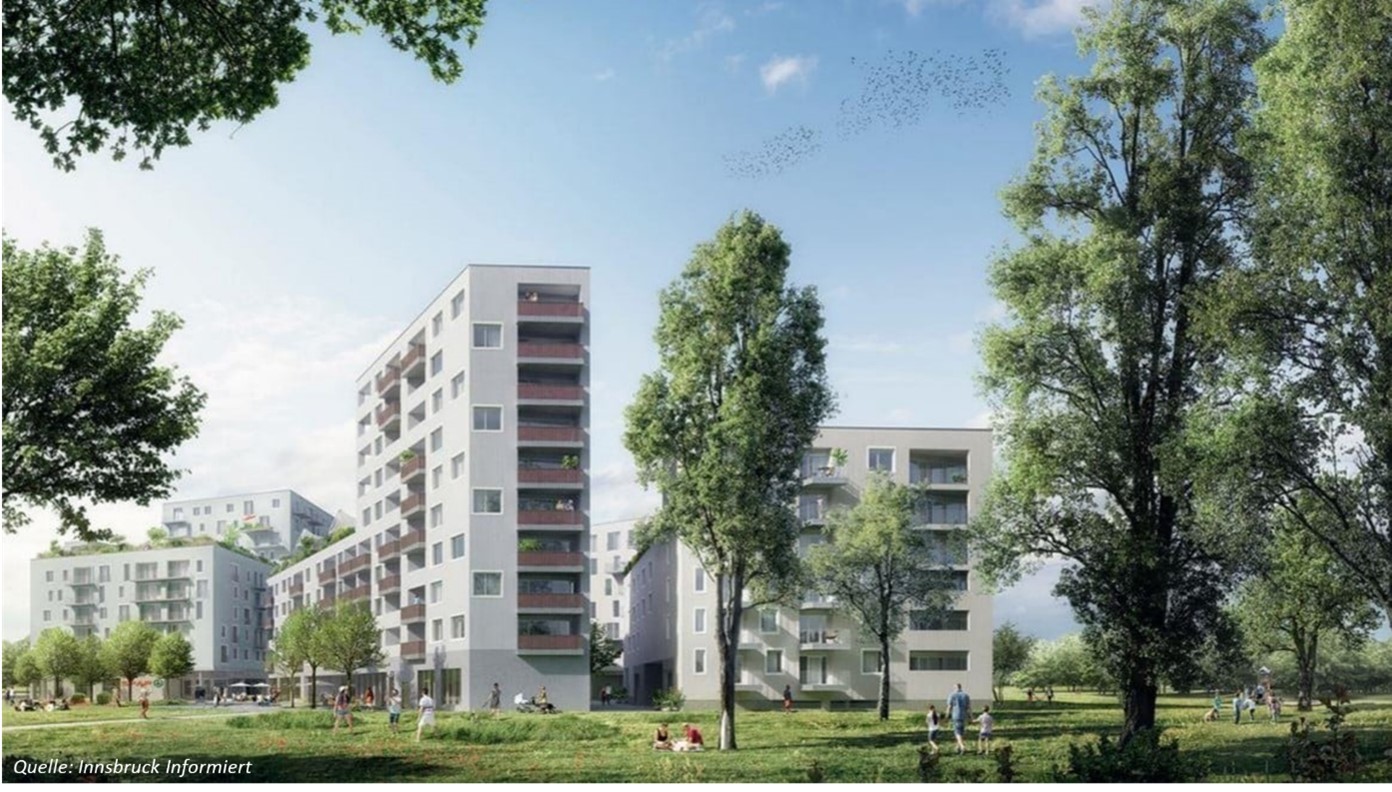
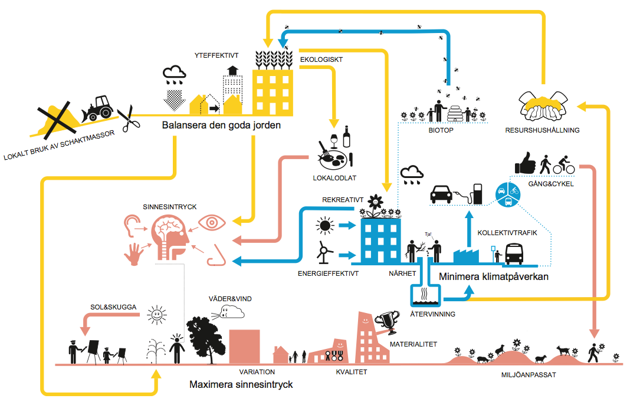
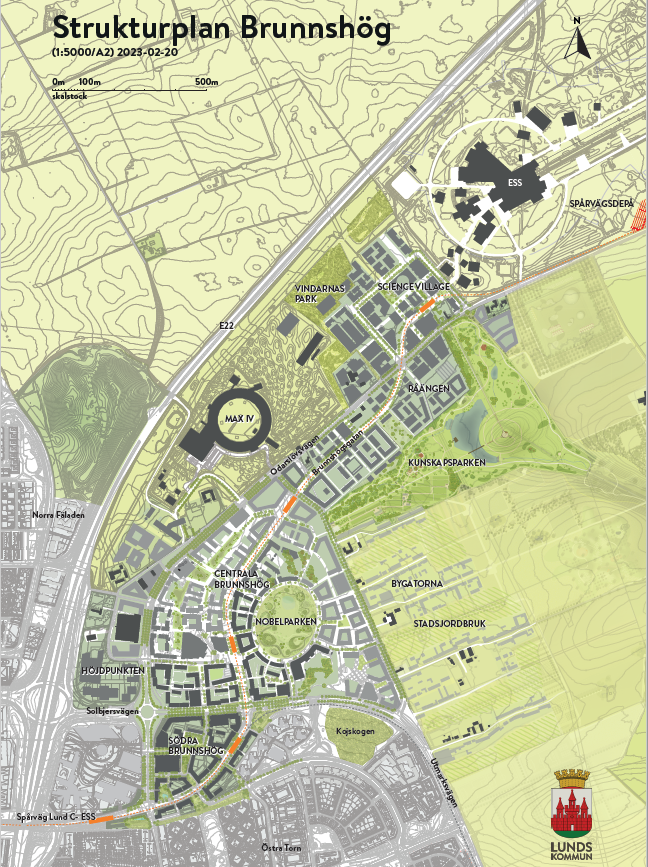
| Lund, Brunnshög district | PED Case Study | Uncompare | |
| Vienna, Am Kempelenpark | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Évora, Portugal | POCITYF – A POsitive Energy CITY Transformation Framework | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Kladno, Sletiště (Sport Area), PED Winter Stadium | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Groningen, PED South | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Lab | Compare |
| Groningen, PED North | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Lab | Compare |
| Maia, Sobreiro Social Housing | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Lab | Uncompare |
| Lubia (Soria), CEDER-CIEMAT | PED Lab | Compare | |
| Tampere, Ilokkaanpuisto district | STARDUST – Holistic and Integrated Urban Model for Smart Cities | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Leon, Former Sugar Factory district | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Istanbul, Kadikoy district, Caferaga | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Espoo, Leppävaara district, Sello center | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Espoo, Espoonlahti district, Lippulaiva block | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Salzburg, Gneis district | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Barcelona, Santa Coloma de Gramenet | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Tartu, City centre area | SmartEnCity – Towards Smart Zero CO2 Cities across Europe | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Bologna, Pilastro-Roveri district | GRETA – GReen Energy Transition Actions | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Barcelona, SEILAB & Energy SmartLab | PED Lab | Compare | |
| Leipzig, Baumwollspinnerei district | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Kifissia, Energy community | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Title | Espoo, Kera | Uden, Loopkantstraat | Vienna, Kriegerheimstätten | Lund, Brunnshög district | Vienna, 16. District, Leben am Wilhelminenberg | Innsbruck, Campagne-Areal | Maia, Sobreiro Social Housing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1P001: Name of the PED case study / PED Lab | |||||||
| A1P001: Name of the PED case study / PED Lab | Espoo, Kera | Uden, Loopkantstraat | Vienna, Kriegerheimstätten | Lund, Brunnshög district | Vienna, 16. District, Leben am Wilhelminenberg | Innsbruck, Campagne-Areal | Maia, Sobreiro Social Housing |
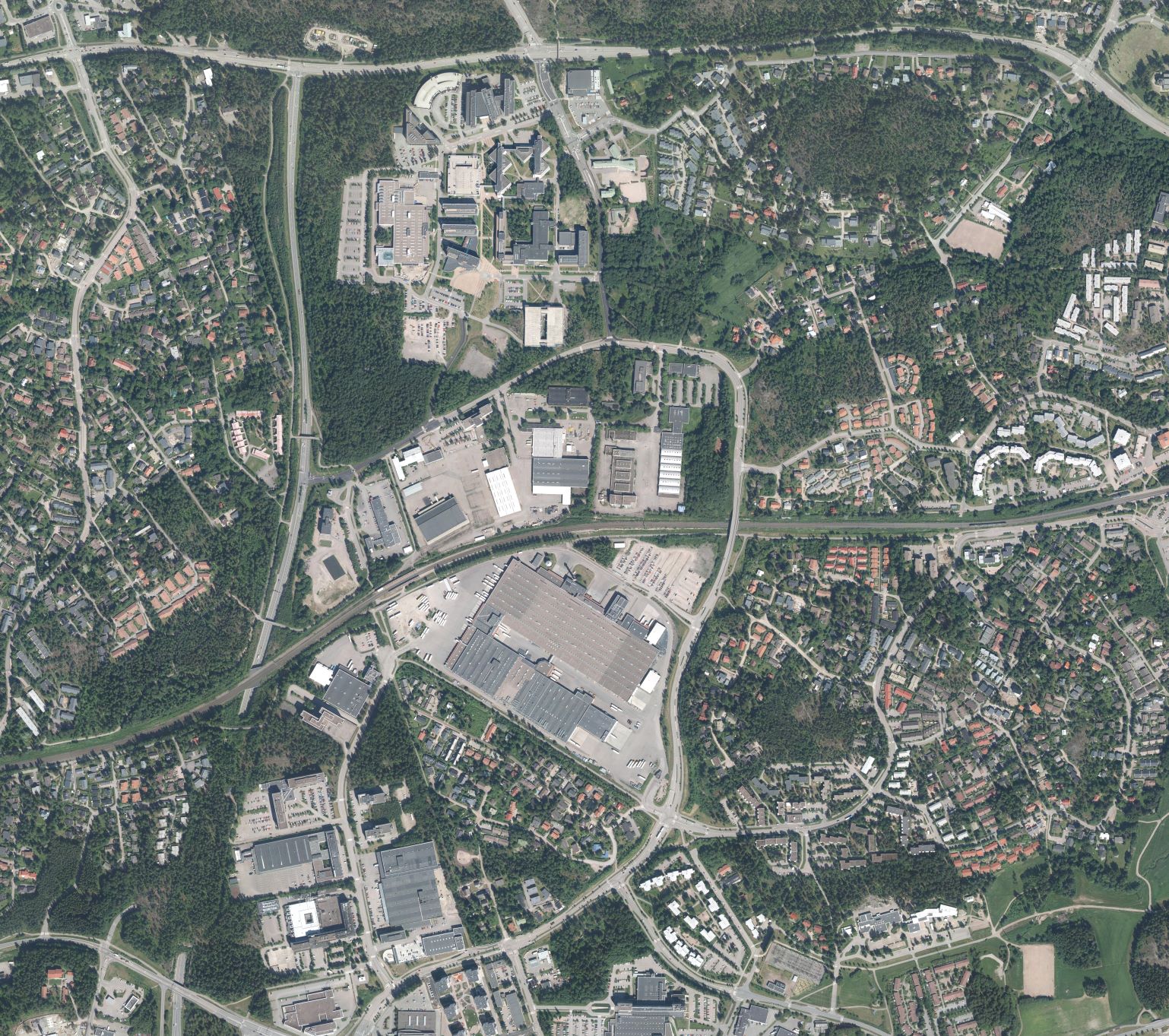
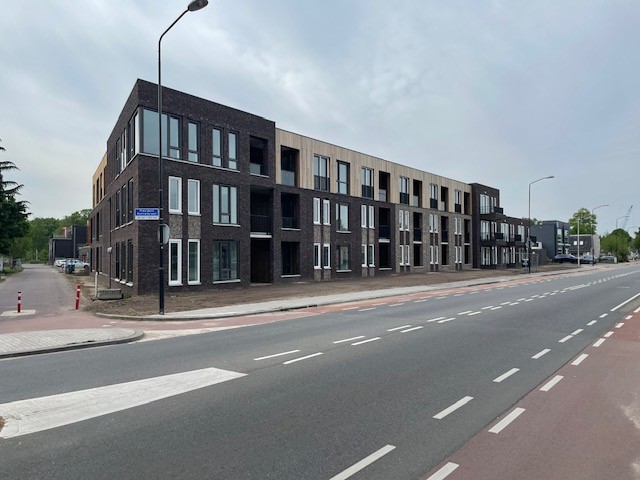
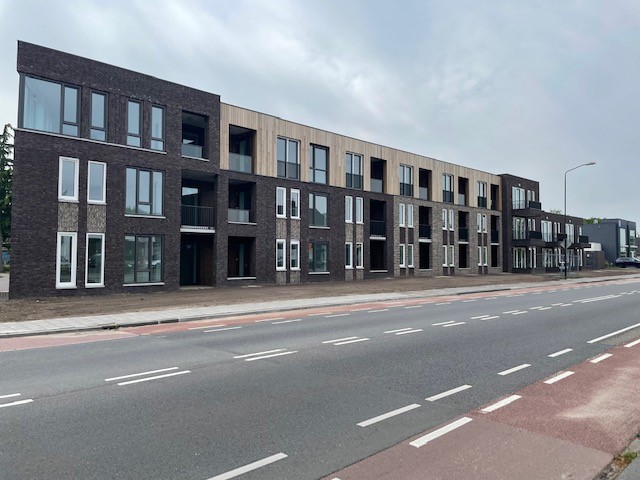
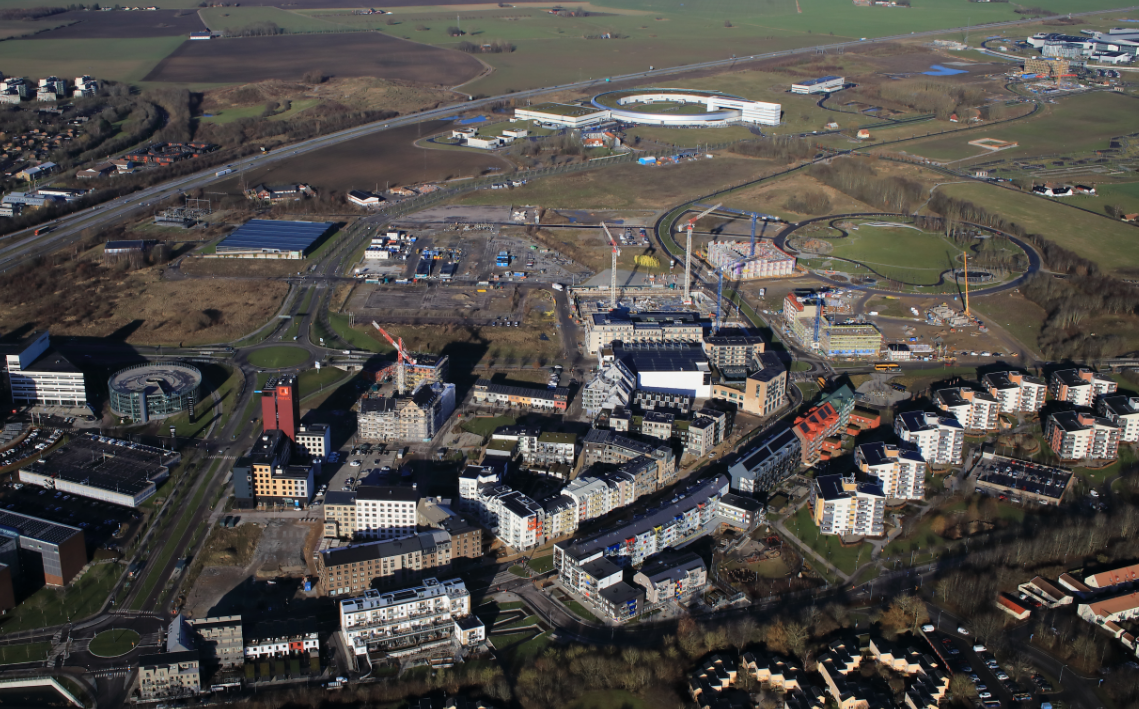
| A1P002: Map / aerial view / photos / graphic details / leaflet | |||||||
| A1P002: Map / aerial view / photos / graphic details / leaflet |
|
|
| ||||
| A1P003: Categorisation of the PED site | |||||||
| PED case study | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| PED relevant case study | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | yes | no |
| PED Lab. | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A1P004: Targets of the PED case study / PED Lab | |||||||
| Climate neutrality | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Annual energy surplus | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | no |
| Energy community | no | no | no | yes | yes | no | no |
| Circularity | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| Air quality and urban comfort | no | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| Electrification | no | yes | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| Net-zero energy cost | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| Net-zero emission | no | no | no | yes | no | yes | no |
| Self-sufficiency (energy autonomous) | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| Maximise self-sufficiency | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| Other | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| Other (A1P004) | Holistic approach on city planning; Minimise car traffic - walkability; Local service; Climate neutral buildings 2030; | ||||||
| A1P005: Phase of the PED case study / PED Lab | |||||||
| A1P005: Project Phase of your case study/PED Lab | Planning Phase | In operation | Planning Phase | In operation | Planning Phase | Completed | Planning Phase |
| A1P006: Start Date | |||||||
| A1P006: Start date | 01/15 | 06/17 | 01/23 | 2015 | 03/24 | 04/16 | 10/21 |
| A1P007: End Date | |||||||
| A1P007: End date | 12/35 | 05/23 | 12/30 | 2040 | 12/27 | 04/22 | 10/24 |
| A1P008: Reference Project | |||||||
| A1P008: Reference Project | |||||||
| A1P009: Data availability | |||||||
| A1P009: Data availability |
|
| |||||
| A1P009: Other | GIS open dataset is under construction | ||||||
| A1P010: Sources | |||||||
| Any publication, link to website, deliverable referring to the PED/PED Lab |
|
| |||||
| A1P011: Geographic coordinates | |||||||
| X Coordinate (longitude): | 24.75377778 | 5.6191 | 16.475416 | 13.232469400769599 | 16.303112 | 11.424346738140256 | -8.373557 |
| Y Coordinate (latitude): | 60.21622222 | 51.6606 | 48.234011 | 55.71989792207193 | 48.218501 | 47.271470786729104 | 41.135804 |
| A1P012: Country | |||||||
| A1P012: Country | Finland | Netherlands | Austria | Sweden | Austria | Austria | Portugal |
| A1P013: City | |||||||
| A1P013: City | Espoo | Uden | Vienna | Lund | Vienna | Innsbruck | Maia |
| A1P014: Climate Zone (Köppen Geiger classification) | |||||||
| A1P014: Climate Zone (Köppen Geiger classification). | Dfb | Cfb | Cfb | Dfb | Cfb | Dfb | Csb |
| A1P015: District boundary | |||||||
| A1P015: District boundary | Geographic | Geographic | Geographic | Geographic | Virtual | Geographic | Virtual |
| Other | |||||||
| A1P016: Ownership of the case study/PED Lab | |||||||
| A1P016: Ownership of the case study/PED Lab: | Mixed | Private | Private | Public | Private | Mixed | Public |
| A1P017: Ownership of the land / physical infrastructure | |||||||
| A1P017: Ownership of the land / physical infrastructure: | Multiple Owners | Single Owner | Single Owner | Multiple Owners | Multiple Owners | Multiple Owners | Multiple Owners |
| A1P018: Number of buildings in PED | |||||||
| A1P018: Number of buildings in PED | 1 | 200 | 4 | 22 | |||
| A1P019: Conditioned space | |||||||
| A1P019: Conditioned space [m²] | 2360 | 1500000 | 22277 | ||||
| A1P020: Total ground area | |||||||
| A1P020: Total ground area [m²] | 580000 | 3860 | 124000 | 1500000 | 11351 | ||
| A1P021: Floor area ratio: Conditioned space / total ground area | |||||||
| A1P021: Floor area ratio: Conditioned space / total ground area | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| A1P022: Financial schemes | |||||||
| A1P022a: Financing - PRIVATE - Real estate | no | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no |
| A1P022a: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 7804440 | 99999999 | |||||
| A1P022b: Financing - PRIVATE - ESCO scheme | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022b: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | |||||||
| A1P022c: Financing - PRIVATE - Other | no | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| A1P022c: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | |||||||
| A1P022d: Financing - PUBLIC - EU structural funding | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A1P022d: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 1000000 | ||||||
| A1P022e: Financing - PUBLIC - National funding | no | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A1P022e: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 30000000 | ||||||
| A1P022f: Financing - PUBLIC - Regional funding | no | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A1P022f: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 30000000 | ||||||
| A1P022g: Financing - PUBLIC - Municipal funding | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A1P022g: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 180000000 | ||||||
| A1P022h: Financing - PUBLIC - Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022h: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | |||||||
| A1P022i: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - EU | no | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A1P022i: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 2000000 | ||||||
| A1P022j: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - National | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no |
| A1P022j: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | |||||||
| A1P022k: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - Local/regional | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022k: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | |||||||
| A1P022l: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022l: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | |||||||
| A1P022: Other | Multiple different funding schemes depending on the case. | ||||||
| A1P023: Economic Targets | |||||||
| A1P023: Economic Targets |
|
|
|
| |||
| A1P023: Other | Circular economy | World class sustainable living and research environments | Create affordable appartments for the citizens | ||||
| A1P024: More comments: | |||||||
| A1P024: More comments: | The project is a follow-up from the “Social Beautiful” concept which was developed in collaboration between Labyrint (Support in sheltered housing), Area (housing company), the municipality of Uden, and Hendriks Coppelmans (developer). The concept aims to provide an answer to changes in various policy areas and the changing demands of society. The Social Beautiful concept consists of the following elements: 1. Living, working, and community services are brought together in one location. A multifunctional residential and service centre is being realized at the location. 2. Housing is shaped by the realization of financially accessible homes suitable for the target group. The housing design is tailored to the target group. it may also include sheltered / protected living. 3. Work takes place at the location or from the same location. The work has a social function within the neighbourhood. Wage-related work must contribute to providing structure in the daily activities of the residents. 4. Neighbourhood management is organized from the location in the surrounding neighbourhood. A service package is provided from the residential and service centre that contributes to the ability of neighbourhood residents to live independently for longer, to strengthen the social network, and to improve the quality of life and safety in the neighbourhood. 5. The houses are suitable for use at all times for regular rental. Communal facilities must be realized within the contours of a regular apartment. The objective is to offer a suitable living and working situation to a group of vulnerable citizens. In this way they become a fully-fledged part of society. They not only make use of the facilities themselves, but also give substance to the level of facilities in the municipality. Due to the integrated approach, they experience a greater sense of well-being and security. | Owners are two local social housing companies. The complete district will consist 4 building blocks, from which only the first one with 4 building is ready built and occupied. At the end, it would be a district of ca. 1100 flats in 16 buildings with 78000 m2 | |||||
| A1P025: Estimated PED case study / PED LAB costs | |||||||
| A1P025: Estimated PED case study / PED LAB costs [mil. EUR] | 7804440 | ||||||
| Contact person for general enquiries | |||||||
| A1P026: Name | Joni Mäkinen | Tonje Healey Trulsrud | Gerhard Hofer (e7 GmbH) | Markus Paulsson | Rachel Leutgöb (e7) | Georgios Dermentzis | Adelina Rodrigues |
| A1P027: Organization | City of Espoo | Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) | e7 GmbH | City of Lund | e7 GmbH | University of Innsbruck | Maia Municipality (CM Maia) – Energy and Mobility division |
| A1P028: Affiliation | Municipality / Public Bodies | Research Center / University | SME / Industry | Municipality / Public Bodies | Research Center / University | Research Center / University | Municipality / Public Bodies |
| A1P028: Other | |||||||
| A1P029: Email | joni.makinen@espoo.fi | tonje.h.trulsrud@ntnu.no | gerhard.hofer@e-sieben.at | markus.paulsson@lund.se | rachel.leutgoeb@e-sieben.at | Georgios.Dermentzis@uibk.ac.at | dscm.adelina@cm-maia.pt |
| Contact person for other special topics | |||||||
| A1P030: Name | Eva Dalman | Carolina Gonçalves (AdEPorto) | |||||
| A1P031: Email | eva.dalman@lund.se | carolinagoncalves@adeporto.eu | |||||
| Pursuant to the General Data Protection Regulation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| A2P001: Fields of application | |||||||
| A2P001: Fields of application |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| A2P001: Other | Reducing CO2eq Emissions | Walkability and biking | |||||
| A2P002: Tools/strategies/methods applied for each of the above-selected fields | |||||||
| A2P002: Tools/strategies/methods applied for each of the above-selected fields | - Kera development commitment (https://www.espoo.fi/en/kera-development-commitment). - SPARCS Co-creation model for sustainable and smart urban areas (www.co-creatingsparcs.fi/en). - Kera area carbon neutrality roadmap (https://static.espoo.fi/cdn/ff/MHDdcMNJ9aYn7CjpoD4zNpo5M-M9HIDLXlJdUrUmf-8/1642756766/public/2022-01/Kera%20carbon%20neutrality%20map_EN.pdf) | Energy efficiency: Energy efficient envelope, with good insulation, triple glazing windows and airtight envelope. (EPC = 0) Energy Flexibility: MCP controls for the heat pump in the apartments. Energy production: PV panels on the roof, Ground source heat pumps Waste management: construction waste was kept to a minimum and sorted and collected separately as much as possible. Indoor air quality: Exhaust ventilation and opening of windows Construction materials: low carbon emission building materials | LundaMaTs methodology for traffic and city planning. LundaEko - Lund's programme for ecological sustainability. Municipally owned land is sold to property developers on environmental conditions. | The buildings are designed based on Passive House standards and dynamic building and system simulations are performed to optimise the HVAC systems, that are a ground-water heat pump for space heating and district heating for domestic hot water preparation. Photovoltaic systems are installed in the available roof spaces, however, more renewable sources are required due to very large number of apartments (very high density) to reach PED, and thus, simulation studies are performed. | Energy production: - installation of photovoltaic systems for renewable on-site energy production; - installation of a BIPV demonstrator for the City Hall building. Energy flexibility: - implementation of an energy community through an active citizens involvement process. Digital technologies: - smart-meters installation in some dwellings in order to monitor consumption and suggest more sustainable energy behaviours. [PCP] Through https://balcaodigital.e-redes.pt/consumptions/history “Espaço Municipal” (https://www.espacomunicipal.pt/pt/) might access history of consumption up to midnight of the previous day. E-mobility: - Installation of new charging stations for electric vehicles; Urban comfort and air quality: - Monitoring units for air pollutants concentration (PM2.5, PM10, NO2) [PCP] Currently we are monitoring CO, O3, NO2, SO2, noise, PM2.5 and PM10 at a point 267 m east from the four buildings southeast of Sobreiro area: | ||
| A2P003: Application of ISO52000 | |||||||
| A2P003: Application of ISO52000 | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| A2P004: Appliances included in the calculation of the energy balance | |||||||
| A2P004: Appliances included in the calculation of the energy balance | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| A2P005: Mobility included in the calculation of the energy balance | |||||||
| A2P005: Mobility included in the calculation of the energy balance | No | No | Yes | No | No | ||
| A2P006: Description of how mobility is included (or not included) in the calculation | |||||||
| A2P006: Description of how mobility is included (or not included) in the calculation | not included | Today electrically charged vehicles are included in the energy balance. In the future also other fuels should be included. | |||||
| A2P007: Annual energy demand in buildings / Thermal demand | |||||||
| A2P007: Annual energy demand in buildings / Thermal demand [GWh/annum] | 54.5 | 0.148 | 4.97 | 25 | 1 | 0.39 | |
| A2P008: Annual energy demand in buildings / Electric Demand | |||||||
| A2P008: Annual energy demand in buildings / Electric Demand [GWh/annum] | 19.4 | 0.109 | 0.75 | 30 | 0.655 | ||
| A2P009: Annual energy demand for e-mobility | |||||||
| A2P009: Annual energy demand for e-mobility [GWh/annum] | 0 | ||||||
| A2P010: Annual energy demand for urban infrastructure | |||||||
| A2P010: Annual energy demand for urban infrastructure [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P011: Annual renewable electricity production on-site during target year | |||||||
| A2P011: PV | yes | yes | no | yes | no | yes | yes |
| A2P011: PV - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | 4 | 0.058 | 0.42 | ||||
| A2P011: Wind | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Wind - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P011: Hydro | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Hydro - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P011: Biomass_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Biomass_el - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P011: Biomass_peat_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Biomass_peat_el - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P011: PVT_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: PVT_el - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P011: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Other - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P012: Annual renewable thermal production on-site during target year | |||||||
| A2P012: Geothermal | no | yes | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Geothermal: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P012: Solar Thermal | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P012 - Solar Thermal: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P012: Biomass_heat | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Biomass_heat: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P012: Waste heat+HP | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Waste heat+HP: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | 200 | ||||||
| A2P012: Biomass_peat_heat | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Biomass_peat_heat: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P012: PVT_th | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - PVT_th: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P012: Biomass_firewood_th | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Biomass_firewood_th: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P012: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Other: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P013: Renewable resources on-site - Additional notes | |||||||
| A2P013: Renewable resources on-site - Additional notes | Local energy utility will implement district level thermal solution. First, energy will be produced from waste heat from a local data center. Further thermal solutions are under discussion and development. | *Annual energy use below is presentedin primary energy consumption | |||||
| A2P014: Annual energy use | |||||||
| A2P014: Annual energy use [GWh/annum] | 78.8 | 0.194 | 0.96 | ||||
| A2P015: Annual energy delivered | |||||||
| A2P015: Annual energy delivered [GWh/annum] | 15.4 | 0.0368 | -2 | ||||
| A2P016: Annual non-renewable electricity production on-site during target year | |||||||
| A2P016: Annual non-renewable electricity production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| A2P017: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year | |||||||
| A2P017: Gas | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Gas: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P017: Coal | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Coal: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P017: Oil | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Oil: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P017: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Other: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P018: Annual renewable electricity imports from outside the boundary during target year | |||||||
| A2P018: PV | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - PV: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P018: Wind | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - Wind: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P018: Hydro | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - Hydro: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P018: Biomass_el | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - Biomass_el: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P018: Biomass_peat_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - Biomass_peat_el: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P018: PVT_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - PVT_el: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P018: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - Other: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: Annual renewable thermal imports from outside the boundary during target year | |||||||
| A2P019: Geothermal | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Geothermal: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: Solar Thermal | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Solar Thermal: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: Biomass_heat | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Biomass_heat: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: Waste heat+HP | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Waste heat+HP: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: Biomass_peat_heat | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Biomass_peat_heat: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: PVT_th | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 PVT_th: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: Biomass_firewood_th | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Biomass_firewood_th: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P019: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Other: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | |||||||
| A2P020: Share of RES on-site / RES outside the boundary | |||||||
| A2P020: Share of RES on-site / RES outside the boundary | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A2P021: GHG-balance calculated for the PED | |||||||
| A2P021: GHG-balance calculated for the PED [tCO2/annum] | 450000 | -0.00043 | |||||
| A2P022: KPIs related to the PED case study / PED Lab | |||||||
| A2P022: Safety & Security | Personal Safety | ||||||
| A2P022: Health | Healthy community | indoor air quility (indoor CO2 concentration) - measured on the extract air of the mechanical ventilation system. Relative humidity to avoid mold. | |||||
| A2P022: Education | |||||||
| A2P022: Mobility | Sustainable mobility | Maximum 1/3 transport with car | |||||
| A2P022: Energy | NOn-renewable primary energy balance, renewable energy ratio, grid purchase factor, load cover factor/self-generation, supply cover factor/self-consumption, net energy/net power, peak delivered/peak expoted, total greenhouse gas emission | Yes | Local energy production 150% of energy need | Yes | Space heating demand, thermal energy delivered by district heating, electricity of the heat pump, thermal losses of the pipes, and PV production. | ||
| A2P022: Water | |||||||
| A2P022: Economic development | capital costs, operational cots, overall economic performance (5 KPIs) | ||||||
| A2P022: Housing and Community | demographic composition, diverse community, social cohesion | 50% rental apartments and 50% owner apartments | |||||
| A2P022: Waste | |||||||
| A2P022: Other | Smartness and flecibility, Indoor Environmental Quality, Social performance - Equity (affordable housing, access to servicees and amenitioes, afforability of energy, living conditions, sustinable mobility, universal design) | ||||||
| A2P023: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Energy Generation | |||||||
| A2P023: Photovoltaics | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| A2P023: Solar thermal collectors | no | no | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P023: Wind Turbines | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Geothermal energy system | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | no | no |
| A2P023: Waste heat recovery | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Waste to energy | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Polygeneration | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Co-generation | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Heat Pump | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| A2P023: Hydrogen | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Hydropower plant | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Biomass | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Biogas | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Other | |||||||
| A2P024: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Energy Flexibility | |||||||
| A2P024: A2P024: Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: Energy management system | yes | yes | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: Demand-side management | yes | yes | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P024: Smart electricity grid | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P024: Thermal Storage | no | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | no |
| A2P024: Electric Storage | no | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: District Heating and Cooling | yes | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | no |
| A2P024: Smart metering and demand-responsive control systems | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: P2P – buildings | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no |
| A2P024: Other | |||||||
| A2P025: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Energy Efficiency | |||||||
| A2P025: Deep Retrofitting | no | no | no | no | yes | no | yes |
| A2P025: Energy efficiency measures in historic buildings | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no |
| A2P025: High-performance new buildings | yes | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no |
| A2P025: Smart Public infrastructure (e.g. smart lighting) | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P025: Urban data platforms | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Mobile applications for citizens | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Building services (HVAC & Lighting) | yes | yes | no | yes | no | yes | yes |
| A2P025: Smart irrigation | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Digital tracking for waste disposal | no | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P025: Smart surveillance | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Other | |||||||
| A2P026: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Mobility | |||||||
| A2P026: Efficiency of vehicles (public and/or private) | yes | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P026: Measures to reduce traffic volume (e.g. measure to support public transportation, shared mobility, measure to reduce journeys and distances) | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P026: e-Mobility | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P026: Soft mobility infrastructures and last mile solutions | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P026: Car-free area | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P026: Other | |||||||
| A2P027: Mobility strategies - Additional notes | |||||||
| A2P027: Mobility strategies - Additional notes | Walkability | ||||||
| A2P028: Energy efficiency certificates | |||||||
| A2P028: Energy efficiency certificates | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| A2P028: If yes, please specify and/or enter notes | EPC = 0, energy neutral building | Miljöbyggnad silver/guld | Two buildings are certified "Passive House new build" | The Municipal Buildings have an energy certificate, according to the Portuguese legislation. | |||
| A2P029: Any other building / district certificates | |||||||
| A2P029: Any other building / district certificates | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| A2P029: If yes, please specify and/or enter notes | |||||||
| A3P001: Relevant city /national strategy | |||||||
| A3P001: Relevant city /national strategy |
|
|
|
| |||
| A3P002: Quantitative targets included in the city / national strategy | |||||||
| A3P002: Quantitative targets included in the city / national strategy | City strategy: Net climate neutrality 2030 | ||||||
| A3P003: Strategies towards decarbonization of the gas grid | |||||||
| A3P003: Strategies towards decarbonization of the gas grid |
|
| |||||
| A3P003: Other | No gas grid in Brunnshög | District heating based mainly on heat pumps and renewable sources | At a national level there are some studies regarding the decarbonization of the gas grid, but no concrete strategies so far. | ||||
| A3P004: Identification of needs and priorities | |||||||
| A3P004: Identification of needs and priorities | Local waste heat is utlized to a very large extent. More local electricity production is needed. Need to minimise the use of private cars. | The priority was to eliminate the CO2 emissions by optimizing the building envelope and the heating systems. | |||||
| A3P005: Sustainable behaviour | |||||||
| A3P005: Sustainable behaviour | Need to minimise the use of private cars. Need to provide efficient methods for sorce separated waste collection. | ||||||
| A3P006: Economic strategies | |||||||
| A3P006: Economic strategies |
|
|
|
|
| ||
| A3P006: Other | Attractivenes | ||||||
| A3P007: Social models | |||||||
| A3P007: Social models |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| A3P007: Other | |||||||
| A3P008: Integrated urban strategies | |||||||
| A3P008: Integrated urban strategies |
|
|
|
| |||
| A3P008: Other | |||||||
| A3P009: Environmental strategies | |||||||
| A3P009: Environmental strategies |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| A3P009: Other | |||||||
| A3P010: Legal / Regulatory aspects | |||||||
| A3P010: Legal / Regulatory aspects | The municipality cannot demand a specific energy solution to private property owners. It has to be voluntary and market based solutions. | ||||||
| B1P001: PED/PED relevant concept definition | |||||||
| B1P001: PED/PED relevant concept definition | Implementation of district level heating system to make heating energy positive and expanding local renewable electricity production. | The demonstration projects is a new residential development, which consists of an apartment complex which includes 39 apartments spread over 3 floors. It is a sustainble plus energy neighbouhood, and has reached a plus energy balance on its first year in operation. It has MPC controls on the individual heat pumps to improve the energy flexibility of the apartments. It includes the "social beatiful" concepts with a strong emphasis on the social sustainability of the project. | Vision: The city as a power plant. The ultimate goal is that more energy is produced within the distric boundaries than is being used (heating, electricity & mobility). Energy efficient buildings, efficient mobility, reuse of residual heat and solar electricity are the main methods. | Extremely low building energy demand, the electric energy of the heat pump used for space heating is significantly lower compared to thermal energy for the domestic hot water preparation. | |||
| B1P002: Motivation behind PED/PED relevant project development | |||||||
| B1P002: Motivation behind PED/PED relevant project development | The need for social housing and the ambition to create a great living environment with a high-performance apartment complex, supplied with renewable energy. It results in lower energy bills for the tenants and high-quality homes. | The aim is to build a sustainable city with minimal climate impact and maximum quality of life. PED is an important step to acheive the aims of a very ambitious city development. | Since it is an urban area, with high building and apartment density, the need for CO2 reduction is quite relevant and thus, in new built, the minimization of CO2 emissions is crucial. | ||||
| B1P003: Environment of the case study area | |||||||
| B2P003: Environment of the case study area | Urban area | Suburban area | Urban area | Urban area | |||
| B1P004: Type of district | |||||||
| B2P004: Type of district |
|
|
|
| |||
| B1P005: Case Study Context | |||||||
| B1P005: Case Study Context |
|
|
|
| |||
| B1P006: Year of construction | |||||||
| B1P006: Year of construction | 2022 | ||||||
| B1P007: District population before intervention - Residential | |||||||
| B1P007: District population before intervention - Residential | 0 | ||||||
| B1P008: District population after intervention - Residential | |||||||
| B1P008: District population after intervention - Residential | 14000 | 18000 | 780 | ||||
| B1P009: District population before intervention - Non-residential | |||||||
| B1P009: District population before intervention - Non-residential | 2000 | ||||||
| B1P010: District population after intervention - Non-residential | |||||||
| B1P010: District population after intervention - Non-residential | 10000 | 22000 | |||||
| B1P011: Population density before intervention | |||||||
| B1P011: Population density before intervention | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B1P012: Population density after intervention | |||||||
| B1P012: Population density after intervention | 0.041379310344828 | 0 | 0 | 0.026666666666667 | 0 | 0.068716412650868 | 0 |
| B1P013: Building and Land Use before intervention | |||||||
| B1P013: Residential | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Residential: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P013: Office | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Office: Specify the sqm [m²] | 60000 | ||||||
| B1P013: Industry and Utility | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Industry and Utility: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P013: Commercial | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Commercial: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P013: Institutional | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Institutional: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P013: Natural areas | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Natural areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | 2000000 | ||||||
| B1P013: Recreational | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Recreational: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P013: Dismissed areas | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Dismissed areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P013: Other | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Other: Specify the sqm [m²] | Outdoor parking: 100000 | ||||||
| B1P014: Building and Land Use after intervention | |||||||
| B1P014: Residential | yes | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no |
| B1P014 - Residential: Specify the sqm [m²] | 2394 | 600000 | |||||
| B1P014: Office | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Office: Specify the sqm [m²] | 650000 | ||||||
| B1P014: Industry and Utility | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Industry and Utility: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P014: Commercial | yes | no | no | no | no | yes | no |
| B1P014 - Commercial: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P014: Institutional | no | no | no | yes | no | yes | no |
| B1P014 - Institutional: Specify the sqm [m²] | 50000 | ||||||
| B1P014: Natural areas | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Natural areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P014: Recreational | yes | no | no | yes | no | yes | no |
| B1P014 - Recreational: Specify the sqm [m²] | 400000 | ||||||
| B1P014: Dismissed areas | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Dismissed areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B1P014: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Other: Specify the sqm [m²] | |||||||
| B2P001: PED Lab concept definition | |||||||
| B2P001: PED Lab concept definition | |||||||
| B2P002: Installation life time | |||||||
| B2P002: Installation life time | Permanent installation | ||||||
| B2P003: Scale of action | |||||||
| B2P003: Scale | Virtual | ||||||
| B2P004: Operator of the installation | |||||||
| B2P004: Operator of the installation | CM Maia, IPMAIA, NEW, AdEP. | ||||||
| B2P005: Replication framework: Applied strategy to reuse and recycling the materials | |||||||
| B2P005: Replication framework: Applied strategy to reuse and recycling the materials | |||||||
| B2P006: Circular Economy Approach | |||||||
| B2P006: Do you apply any strategy to reuse and recycling the materials? | No | ||||||
| B2P006: Other | |||||||
| B2P007: Motivation for developing the PED Lab | |||||||
| B2P007: Motivation for developing the PED Lab |
| ||||||
| B2P007: Other | |||||||
| B2P008: Lead partner that manages the PED Lab | |||||||
| B2P008: Lead partner that manages the PED Lab | Municipality | ||||||
| B2P008: Other | |||||||
| B2P009: Collaborative partners that participate in the PED Lab | |||||||
| B2P009: Collaborative partners that participate in the PED Lab |
| ||||||
| B2P009: Other | Energy Agency | ||||||
| B2P010: Synergies between the fields of activities | |||||||
| B2P010: Synergies between the fields of activities | |||||||
| B2P011: Available facilities to test urban configurations in PED Lab | |||||||
| B2P011: Available facilities to test urban configurations in PED Lab |
| ||||||
| B2P011: Other | |||||||
| B2P012: Incubation capacities of PED Lab | |||||||
| B2P012: Incubation capacities of PED Lab |
| ||||||
| B2P013: Availability of the facilities for external people | |||||||
| B2P013: Availability of the facilities for external people | Depends on the building: _Tecmaia is open to the public but the buildings are for the exclusive use of companies allocated at the industrial site; _The municipal buildings have public access; _The residential buildings have an exclusive use for the residents. | ||||||
| B2P014: Monitoring measures | |||||||
| B2P014: Monitoring measures |
| ||||||
| B2P015: Key Performance indicators | |||||||
| B2P015: Key Performance indicators |
| ||||||
| B2P016: Execution of operations | |||||||
| B2P016: Execution of operations | Current PED status (WP5 SPARCS): Conceptualization and methodology definition of the (virtual) PED for Maia Municipality with real monitoring and assessment in order to replicate and scale up to a city-level PED. The financial investments were already targeted. | ||||||
| B2P017: Capacities | |||||||
| B2P017: Capacities | _Energy production and storage, _Monitoring; _Digitization. | ||||||
| B2P018: Relations with stakeholders | |||||||
| B2P018: Relations with stakeholders | The relationship with stakeholders (municipal companies, industry, citizens, etc) has been fundamental for the definition of the PED. In this sense, some sessions were organized to gather different points of view in order to trace the best path for the PED. Also, the participation of Maia Municipality in EU projects, as EHHUR and OMEGA-X, makes possible the share of knowledge between different partners. | ||||||
| B2P019: Available tools | |||||||
| B2P019: Available tools |
| ||||||
| B2P019: Available tools | |||||||
| B2P020: External accessibility | |||||||
| B2P020: External accessibility | |||||||
| C1P001: Unlocking Factors | |||||||
| C1P001: Recent technological improvements for on-site RES production | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Innovative, integrated, prefabricated packages for buildings envelope / Energy efficiency of building stock | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Energy Communities, P2P, Prosumers concepts | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Storage systems and E-mobility market penetration | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Decreasing costs of innovative materials | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P001: Financial mechanisms to reduce costs and maximize benefits | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: The ability to predict Multiple Benefits | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: The ability to predict the distribution of benefits and impacts | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Citizens improved awareness and engagement on sustainable energy issues (bottom-up) | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Social acceptance (top-down) | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Improved local and national policy frameworks (i.e. incentives, laws etc.) | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Presence of integrated urban strategies and plans | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important |
| C1P001: Multidisciplinary approaches available for systemic integration | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Availability of grants (from EC or other donors) to finance the PED Lab projects | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Availability of RES on site (Local RES) | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Ongoing or established collaboration on Public Private Partnership among key stakeholders | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Any other UNLOCKING FACTORS | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P001: Any other UNLOCKING FACTORS (if any) | |||||||
| C1P002: Driving Factors | |||||||
| C1P002: Climate Change adaptation need | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important |
| C1P002: Climate Change mitigation need (local RES production and efficiency) | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important |
| C1P002: Rapid urbanization trend and need of urban expansions | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P002: Urban re-development of existing built environment | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P002: Economic growth need | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P002: Improved local environmental quality (air, noise, aesthetics, etc.) | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important |
| C1P002: Territorial and market attractiveness | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 4 - Important |
| C1P002: Energy autonomy/independence | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important |
| C1P002: Any other DRIVING FACTOR | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P002: Any other DRIVING FACTOR (if any) | |||||||
| C1P003: Administrative barriers | |||||||
| C1P003: Difficulty in the coordination of high number of partners and authorities | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important |
| C1P003: Lack of good cooperation and acceptance among partners | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important |
| C1P003: Lack of public participation | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P003: Lack of institutions/mechanisms to disseminate information | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P003:Long and complex procedures for authorization of project activities | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P003: Time consuming requirements by EC or other donors concerning reporting and accountancy | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P003: Complicated and non-comprehensive public procurement | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P003: Fragmented and or complex ownership structure | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P003: City administration & cross-sectoral attitude/approaches (silos) | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P003: Lack of internal capacities to support energy transition | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P003: Any other Administrative BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P003: Any other Administrative BARRIER (if any) | Delay in the Environmental Dialogue processing in the municipality | ||||||
| C1P004: Policy barriers | |||||||
| C1P004: Lack of long-term and consistent energy plans and policies | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P004: Lacking or fragmented local political commitment and support on the long term | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P004: Lack of Cooperation & support between national-regional-local entities | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P004: Any other Political BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P004: Any other Political BARRIER (if any) | |||||||
| C1P005: Legal and Regulatory barriers | |||||||
| C1P005: Inadequate regulations for new technologies | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Regulatory instability | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Non-effective regulations | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Unfavorable local regulations for innovative technologies | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Building code and land-use planning hindering innovative technologies | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Insufficient or insecure financial incentives | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Unresolved privacy concerns and limiting nature of privacy protection regulation | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Shortage of proven and tested solutions and examples | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P005: Any other Legal and Regulatory BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P005: Any other Legal and Regulatory BARRIER (if any) | |||||||
| C1P006: Environmental barriers | |||||||
| C1P006: Environmental barriers | ? | Urban area very high buildings (and apartment) density and thus, less available space for renewable sources. | |||||
| C1P007: Technical barriers | |||||||
| C1P007: Lack of skilled and trained personnel | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Deficient planning | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P007: Retrofitting work in dwellings in occupied state | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Lack of well-defined process | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Inaccuracy in energy modelling and simulation | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Lack/cost of computational scalability | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Grid congestion, grid instability | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Negative effects of project intervention on the natural environment | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P007: Energy retrofitting work in dense and/or historical urban environment | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Difficult definition of system boundaries | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Any other Thecnical BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P007: Any other Thecnical BARRIER (if any) | |||||||
| C1P008: Social and Cultural barriers | |||||||
| C1P008: Inertia | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Lack of values and interest in energy optimization measurements | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Low acceptance of new projects and technologies | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Difficulty of finding and engaging relevant actors | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Lack of trust beyond social network | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P008: Rebound effect | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P008: Hostile or passive attitude towards environmentalism | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Exclusion of socially disadvantaged groups | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Non-energy issues are more important and urgent for actors | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P008: Hostile or passive attitude towards energy collaboration | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Any other Social BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P008: Any other Social BARRIER (if any) | |||||||
| C1P009: Information and Awareness barriers | |||||||
| C1P009: Insufficient information on the part of potential users and consumers | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P009: Perception of interventions as complicated and expensive, with negative socio-economic or environmental impacts | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P009: Lack of awareness among authorities | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P009: Information asymmetry causing power asymmetry of established actors | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P009: High costs of design, material, construction, and installation | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important |
| C1P009: Any other Information and Awareness BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P009: Any other Information and Awareness BARRIER (if any) | |||||||
| C1P010: Financial barriers | |||||||
| C1P010: Hidden costs | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P010: Insufficient external financial support and funding for project activities | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P010: Economic crisis | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important |
| C1P010: Risk and uncertainty | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P010: Lack of consolidated and tested business models | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P010: Limited access to capital and cost disincentives | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P010: Any other Financial BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P010: Any other Financial BARRIER (if any) | |||||||
| C1P011: Market barriers | |||||||
| C1P011: Split incentives | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P011: Energy price distortion | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P011: Energy market concentration, gatekeeper actors (DSOs) | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P011: Any other Market BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P011: Any other Market BARRIER (if any) | |||||||
| C1P012: Stakeholders involved | |||||||
| C1P012: Government/Public Authorities |
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: Research & Innovation |
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: Financial/Funding |
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Analyst, ICT and Big Data |
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Business process management |
|
| |||||
| C1P012: Urban Services providers |
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Real Estate developers |
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: Design/Construction companies |
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: End‐users/Occupants/Energy Citizens |
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: Social/Civil Society/NGOs |
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Industry/SME/eCommerce |
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Other | |||||||
| C1P012: Other (if any) | |||||||
| Summary |

Authors (framework concept)
Beril Alpagut (Demir Energy); Giulia Turci (University of Bologna); Michal Kuzmic (Czech Technical University in Prague); Paolo Civiero (Università Roma Tre); Serena Pagliulia (University of Bologna); Oscar Seco (CIEMAT); Silvia Soutullo (CIEMAT); Daniele Vettorato (EURAC Research, IEA Annex 83); Bailador Ferreras M. Almudena (CIEMAT); Vicky Albert-Seifried (FHG ISE)
Contributors (to the content)
Laura Aelenei (LNEG), Nienke Maas (TNO), Savis Gohari (OsloMet), Andras Reith (ABUD), Ghazal Etminan (AIT), Maria-Beatrice Andreucci (Universita Sapienza), Francesco Reda (VTT, IEA Annex 83), Mari Hukkalainen (VTT), Judith-Borsboom (Locality), Gilda Massa (ENEA), Jelena Ziemele (University of Latvia), Nikola Pokorny (CVUT), Sergio Diaz de Garayo Balsategui (CENER, IEA Annex 83), Matthias Haaze (ZHAW, IEA Annex 83), Christoph Gollner (FFG, JPI UE), Silvia Bossi (ENEA, JPI UE), Christian Winzer (Zurich University of Applied Science), George Martinopoulos (Centre for Research and Technology Hellas), Maria Nuria Sánchez (CIEMAT), Angelina Tomova (Energy Agency of Plovdiv)
Implemented by
Boutik.pt: Filipe Martins, Jamal Khan
Marek Suchánek (Czech Technical University in Prague)