| Name | Project | Type | Compare |
|---|---|---|---|
| Győr Geothermal District Heating Project | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Jacobs Borchs Gate, Drammen | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Dietenbach, Freiburg im Breisgau | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| SmartEnCity, Lecce | SmartEnCity – Towards Smart Zero CO2 Cities across Europe | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| STARDUST, Trento | STARDUST – Holistic and Integrated Urban Model for Smart Cities | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Klimatkontrakt Hyllie, Malmö | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| EnStadt:Pfaff, Kaiserslautern | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| mySMARTlife, Helsinki | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| REPLICATE (pilot action in the Novoli-Cascine district on “le PIagge” buildings), Firenze | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Sinfonia, Bolzano | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Hunziker Areal, Zürich | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Hammarby Sjöstad 2.0, | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Sharing Cities, Milano | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| District Heating Pozo Barredo, Mieres | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Cityfied (demo Linero), Lund | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Smart Otaniemi, Espoo | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| Zukunftsquartier, Vienna | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Santa Chiara Open Lab, Trento | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Barrio La Pinada, Paterna | PED Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| Zero Village Bergen (ZVB) | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Võru +CityxChange | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| NTNU Campus within the Knowledge Axis, Trondheim | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Furuset project, Oslo | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Laser Valley – Land of Lights | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Ydalir project | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| NyBy – Ny Flyplass (New City – New Airport) | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Uncompare |
| Fornebu, Bærum | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Fleuraye west, Carquefou | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Smart Energy Åland | PED Case Study | Uncompare | |
| Romania, Alba Iulia PED | ASCEND – Accelerate poSitive Clean ENergy Districts | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Romania, Alba Iulia PED | InterPED – INTERoperable cloud-based solution for cross-vector planning and management of Positive Energy Districts | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Munich, Harthof district | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Lublin | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Roubaix, MustBe0 – Résidence Philippe le Hardi – 125 Rue d’Oran | CULTURAL-E – Climate and cultural-based solutions for Plus Energy Buildings | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Bærum, Eiksveien 116 | CULTURAL-E – Climate and cultural-based solutions for Plus Energy Buildings | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Findhorn, the Park | InterPED – INTERoperable cloud-based solution for cross-vector planning and management of Positive Energy Districts | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Amsterdam, Buiksloterham PED | ATELIER – AmsTErdam BiLbao cItizen drivEn smaRt cities | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Schönbühel-Aggsbach, Schönbühel an der Donau | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Umeå, Ålidhem district | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Aalborg East | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare | |
| Ankara, Çamlık District | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Trenčín | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Luxembourg, Betzdorf | LEGOFIT – Adaptable technological solutions based on early design actions for the construction and renovation of Energy Positive Homes | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Vantaa, Aviapolis | NEUTRALPATH – Pathway towards Climate-Neutrality through low risky and fully replicable Positive Clean Energy Districts | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Vidin, Himik and Bononia | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Oslo, Verksbyen | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Uden, Loopkantstraat | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Relevant Case Study | Uncompare |
| Zaragoza, Actur | NEUTRALPATH – Pathway towards Climate-Neutrality through low risky and fully replicable Positive Clean Energy Districts | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Aarhus, Brabrand | BIPED – Building Intelligent Positive Energy Districts | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Riga, Ķīpsala, RTU smart student city | ExPEDite – Enabling Positive Energy Districts through Digital Twins | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Izmir, District of Karşıyaka | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Istanbul, Ozyegin University Campus | LEGOFIT – Adaptable technological solutions based on early design actions for the construction and renovation of Energy Positive Homes | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Espoo, Kera | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study / PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Borlänge, Rymdgatan’s Residential Portfolio | PED-ACT – Auto characterization of PEDs for digital references towards iterative process optimisation | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Freiburg, Waldsee | PED urban – Development of methods and tools for accounting, planning and operation of climate-neutral district | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Innsbruck, Campagne-Areal | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Graz, Reininghausgründe | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Stor-Elvdal, Campus Evenstad | ZEN – Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Oulu, Kaukovainio | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Halmstad, Fyllinge | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare | |
| Lund, Brunnshög district | PED Case Study | Uncompare | |
| Vienna, Am Kempelenpark | PED Case Study | Compare | |
| Évora, Portugal | POCITYF – A POsitive Energy CITY Transformation Framework | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Compare |
| Kladno, Sletiště (Sport Area), PED Winter Stadium | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Groningen, PED South | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Lab | Compare |
| Groningen, PED North | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Lab | |
| Maia, Sobreiro Social Housing | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Lab | Compare |
| Lubia (Soria), CEDER-CIEMAT | PED Lab | Compare | |
| Tampere, Ilokkaanpuisto district | STARDUST – Holistic and Integrated Urban Model for Smart Cities | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Leon, Former Sugar Factory district | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Istanbul, Kadikoy district, Caferaga | MAKING-CITY – Energy efficient pathway for the city transformation: enabling a positive future | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Espoo, Leppävaara district, Sello center | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Espoo, Espoonlahti district, Lippulaiva block | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Salzburg, Gneis district | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Case Study | Uncompare |
| Barcelona, Santa Coloma de Gramenet | Syn.ikia – Sustainable Plus Energy Neighbourhoods | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Tartu, City centre area | SmartEnCity – Towards Smart Zero CO2 Cities across Europe | PED Relevant Case Study / PED Lab | Uncompare |
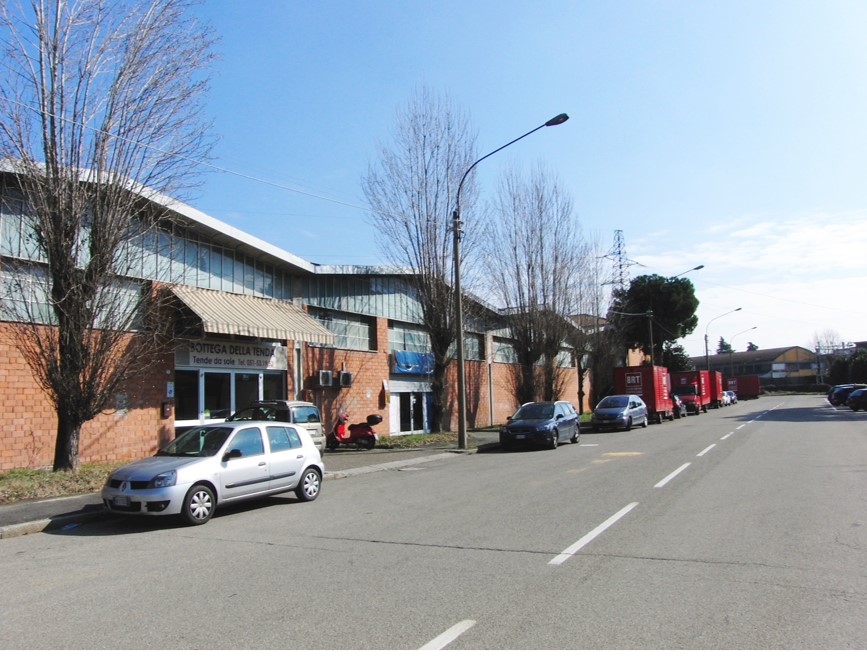
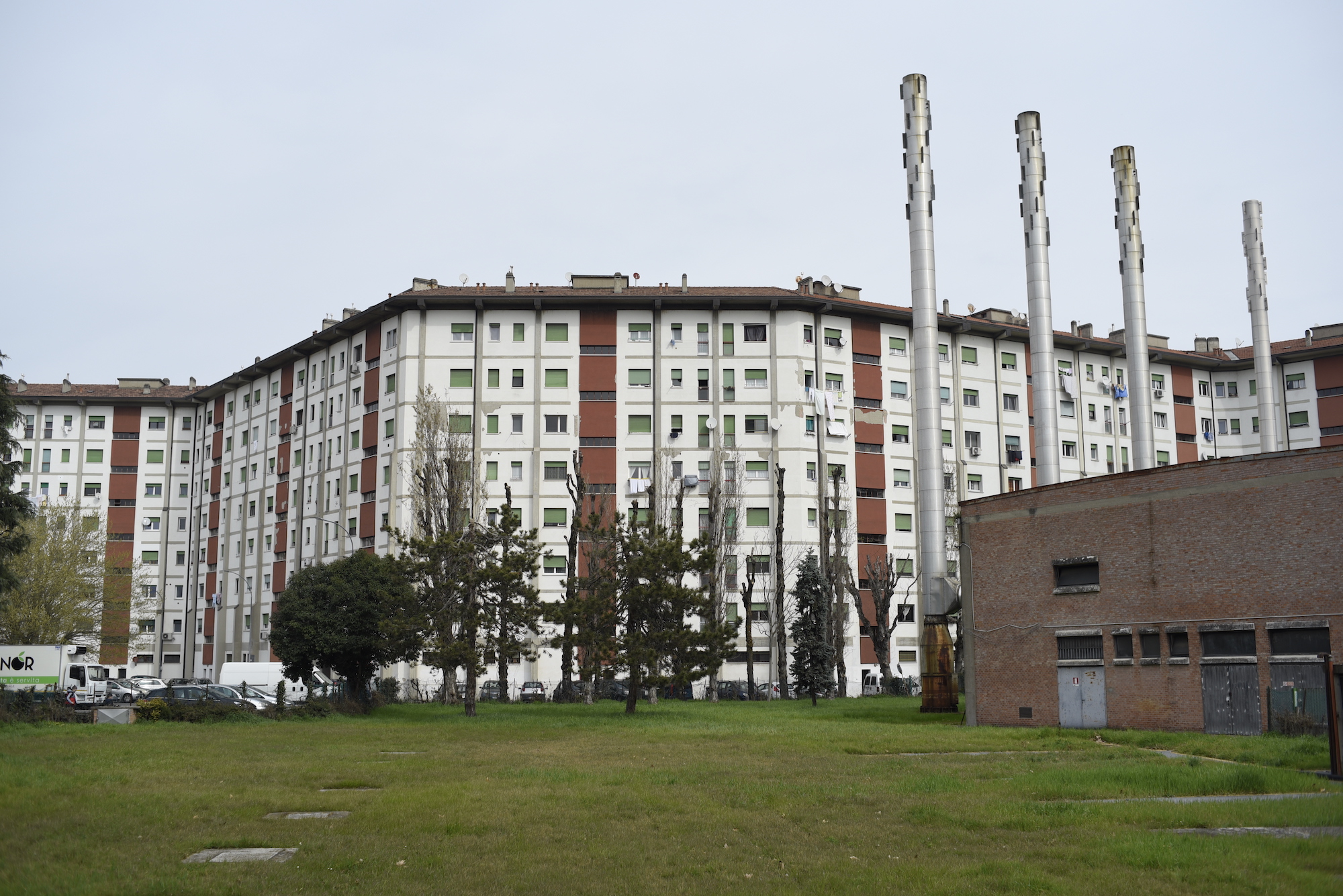
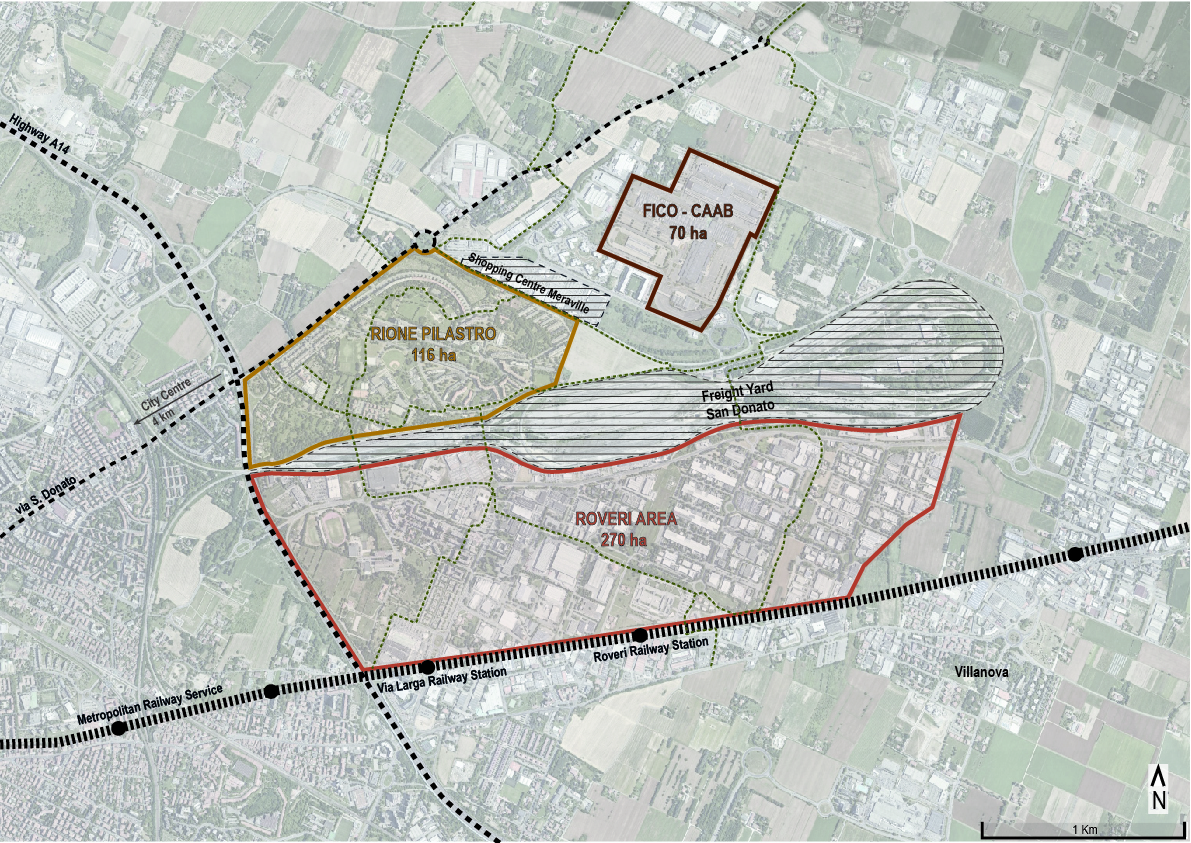
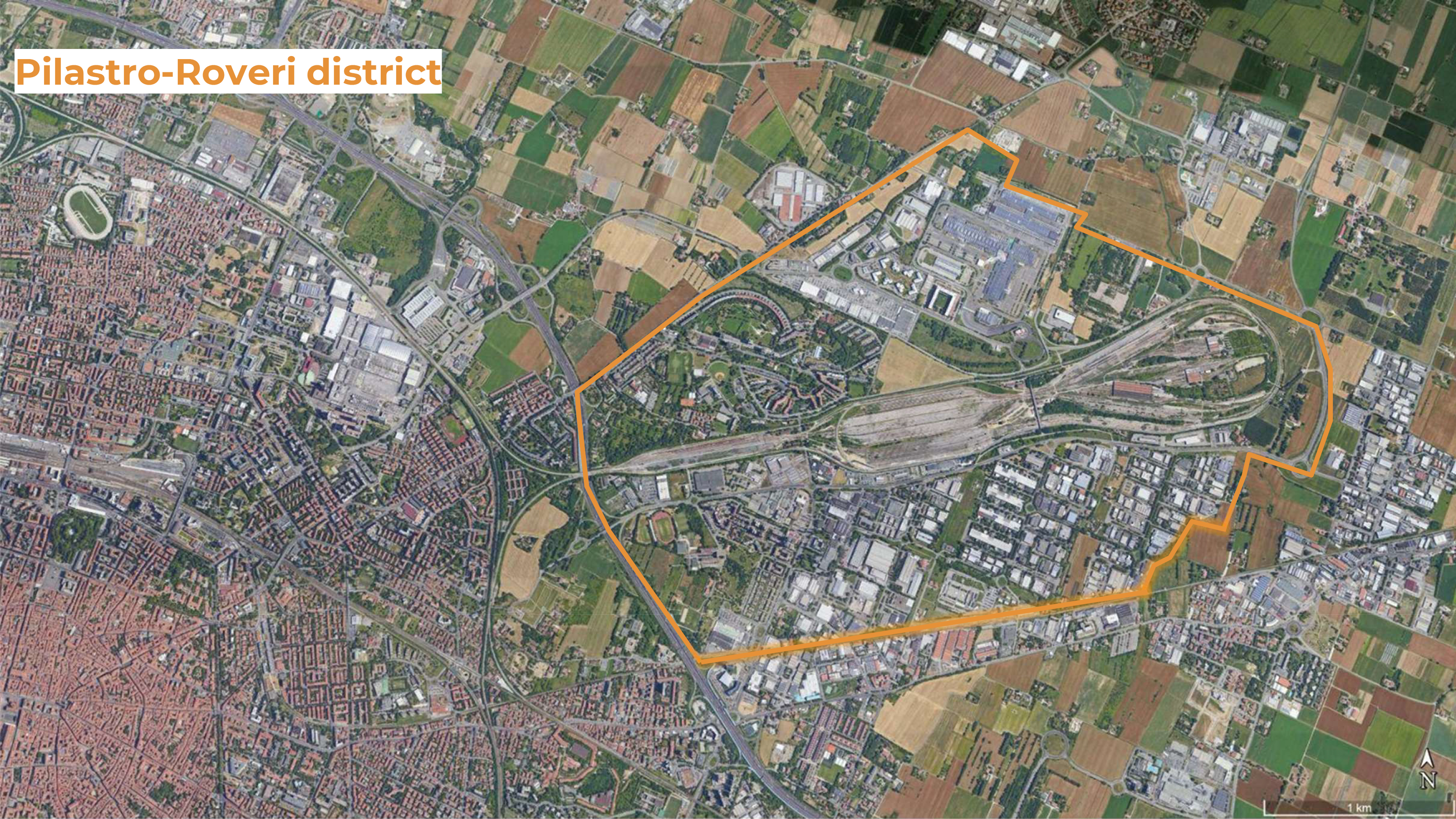
| Bologna, Pilastro-Roveri district | GRETA – GReen Energy Transition Actions | PED Relevant Case Study | Uncompare |
| Barcelona, SEILAB & Energy SmartLab | PED Lab | Compare | |
| Leipzig, Baumwollspinnerei district | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Case Study | Compare |
| Kifissia, Energy community | SPARCS – Sustainable energy Positive & zero cARbon CommunitieS | PED Relevant Case Study | Compare |
| Title | Groningen, PED North | Tartu, City centre area | Uden, Loopkantstraat | Bologna, Pilastro-Roveri district | Smart Energy Åland | Salzburg, Gneis district | NyBy – Ny Flyplass (New City – New Airport) | Lund, Brunnshög district |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1P001: Name of the PED case study / PED Lab | ||||||||
| A1P001: Name of the PED case study / PED Lab | Groningen, PED North | Tartu, City centre area | Uden, Loopkantstraat | Bologna, Pilastro-Roveri district | Smart Energy Åland | Salzburg, Gneis district | NyBy – Ny Flyplass (New City – New Airport) | Lund, Brunnshög district |
| A1P002: Map / aerial view / photos / graphic details / leaflet | ||||||||
| A1P002: Map / aerial view / photos / graphic details / leaflet |
|
|
| |||||
| A1P003: Categorisation of the PED site | ||||||||
| PED case study | no | no | no | no | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| PED relevant case study | no | yes | yes | yes | no | no | no | no |
| PED Lab. | yes | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P004: Targets of the PED case study / PED Lab | ||||||||
| Climate neutrality | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Annual energy surplus | yes | no | yes | no | no | yes | no | yes |
| Energy community | yes | no | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes |
| Circularity | yes | yes | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| Air quality and urban comfort | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no | yes |
| Electrification | no | yes | yes | no | no | no | no | yes |
| Net-zero energy cost | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| Net-zero emission | yes | yes | no | no | no | no | yes | yes |
| Self-sufficiency (energy autonomous) | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no |
| Maximise self-sufficiency | no | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| Other | no | no | no | no | yes | no | yes | yes |
| Other (A1P004) | Energy efficient; Carbon free; Sustainable neighbourhood | Energy efficient; Sustainable neighbourhood; Social aspects/affordability | Holistic approach on city planning; Minimise car traffic - walkability; Local service; Climate neutral buildings 2030; | |||||
| A1P005: Phase of the PED case study / PED Lab | ||||||||
| A1P005: Project Phase of your case study/PED Lab | Implementation Phase | Implementation Phase | In operation | Planning Phase | In operation | Completed | Planning Phase | In operation |
| A1P006: Start Date | ||||||||
| A1P006: Start date | 12/18 | 02/16 | 06/17 | 09/19 | 01/14 | 01/20 | 01/20 | 2015 |
| A1P007: End Date | ||||||||
| A1P007: End date | 12/23 | 07/22 | 05/23 | 10/23 | 01/24 | 2040 | ||
| A1P008: Reference Project | ||||||||
| A1P008: Reference Project | ||||||||
| A1P009: Data availability | ||||||||
| A1P009: Data availability |
|
|
|
| ||||
| A1P009: Other | GIS open dataset is under construction | |||||||
| A1P010: Sources | ||||||||
| Any publication, link to website, deliverable referring to the PED/PED Lab |
|
|
| |||||
| A1P011: Geographic coordinates | ||||||||
| X Coordinate (longitude): | 6.535121 | 26.722737 | 5.6191 | 11.397323 | 19.9438638 | 13.041216 | 14.363169 | 13.232469400769599 |
| Y Coordinate (latitude): | 53.234846 | 58.380713 | 51.6606 | 44.507106 | 60.2166218 | 47.771019 | 67.271954 | 55.71989792207193 |
| A1P012: Country | ||||||||
| A1P012: Country | Netherlands | Estonia | Netherlands | Italy | Finland | Austria | Norway | Sweden |
| A1P013: City | ||||||||
| A1P013: City | Groningen | Tartu | Uden | Bologna | Åland | Salzburg | Bodø | Lund |
| A1P014: Climate Zone (Köppen Geiger classification) | ||||||||
| A1P014: Climate Zone (Köppen Geiger classification). | Cfa | Dfb | Cfb | Cfa | Dfb | Dfb | Dfc | Dfb |
| A1P015: District boundary | ||||||||
| A1P015: District boundary | Functional | Functional | Geographic | Geographic | Functional | Geographic | Geographic | |
| Other | ||||||||
| A1P016: Ownership of the case study/PED Lab | ||||||||
| A1P016: Ownership of the case study/PED Lab: | Mixed | Private | Private | Mixed | Mixed | Mixed | Public | Public |
| A1P017: Ownership of the land / physical infrastructure | ||||||||
| A1P017: Ownership of the land / physical infrastructure: | Multiple Owners | Multiple Owners | Single Owner | Multiple Owners | Multiple Owners | Single Owner | Single Owner | Multiple Owners |
| A1P018: Number of buildings in PED | ||||||||
| A1P018: Number of buildings in PED | 7 | 18 | 1 | 1962 | 17 | 200 | ||
| A1P019: Conditioned space | ||||||||
| A1P019: Conditioned space [m²] | 1.01 | 35217 | 2360 | 199762 | 1500000 | |||
| A1P020: Total ground area | ||||||||
| A1P020: Total ground area [m²] | 17.132 | 793144 | 3860 | 7800000 | 3400000 | 1500000 | ||
| A1P021: Floor area ratio: Conditioned space / total ground area | ||||||||
| A1P021: Floor area ratio: Conditioned space / total ground area | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| A1P022: Financial schemes | ||||||||
| A1P022a: Financing - PRIVATE - Real estate | yes | yes | yes | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A1P022a: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 6500000 | 7804440 | 99999999 | |||||
| A1P022b: Financing - PRIVATE - ESCO scheme | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022b: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | ||||||||
| A1P022c: Financing - PRIVATE - Other | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022c: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | ||||||||
| A1P022d: Financing - PUBLIC - EU structural funding | no | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A1P022d: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 4000000 | 1000000 | ||||||
| A1P022e: Financing - PUBLIC - National funding | yes | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| A1P022e: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 8000000 | 30000000 | ||||||
| A1P022f: Financing - PUBLIC - Regional funding | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| A1P022f: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 30000000 | |||||||
| A1P022g: Financing - PUBLIC - Municipal funding | yes | no | no | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| A1P022g: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 180000000 | |||||||
| A1P022h: Financing - PUBLIC - Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022h: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | ||||||||
| A1P022i: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - EU | yes | no | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes |
| A1P022i: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | 2000000 | |||||||
| A1P022j: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - National | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022j: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | ||||||||
| A1P022k: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - Local/regional | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022k: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | ||||||||
| A1P022l: Financing - RESEARCH FUNDING - Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A1P022l: Add the value in EUR if available [EUR] | ||||||||
| A1P022: Other | ||||||||
| A1P023: Economic Targets | ||||||||
| A1P023: Economic Targets |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| A1P023: Other | Tourism development | Boosting social cooperation and social aid | World class sustainable living and research environments | |||||
| A1P024: More comments: | ||||||||
| A1P024: More comments: | The project is a follow-up from the “Social Beautiful” concept which was developed in collaboration between Labyrint (Support in sheltered housing), Area (housing company), the municipality of Uden, and Hendriks Coppelmans (developer). The concept aims to provide an answer to changes in various policy areas and the changing demands of society. The Social Beautiful concept consists of the following elements: 1. Living, working, and community services are brought together in one location. A multifunctional residential and service centre is being realized at the location. 2. Housing is shaped by the realization of financially accessible homes suitable for the target group. The housing design is tailored to the target group. it may also include sheltered / protected living. 3. Work takes place at the location or from the same location. The work has a social function within the neighbourhood. Wage-related work must contribute to providing structure in the daily activities of the residents. 4. Neighbourhood management is organized from the location in the surrounding neighbourhood. A service package is provided from the residential and service centre that contributes to the ability of neighbourhood residents to live independently for longer, to strengthen the social network, and to improve the quality of life and safety in the neighbourhood. 5. The houses are suitable for use at all times for regular rental. Communal facilities must be realized within the contours of a regular apartment. The objective is to offer a suitable living and working situation to a group of vulnerable citizens. In this way they become a fully-fledged part of society. They not only make use of the facilities themselves, but also give substance to the level of facilities in the municipality. Due to the integrated approach, they experience a greater sense of well-being and security. | The Pilastro-Roveri area is a large peri-urban district in the northeast of the city of Bologna (about 650 hectares). In particular, the northern area is mainly characterised by the residential sector of Rione Pilastro, a significant complex of social housing built in the 1960s in response to the housing emergency due to migrations from southern Italy and nowadays satisfying more global migrations. The southern area is instead characterised by the presence of the production district called Roveri. The area appears relevant for the research as it has several evolution potentials towards a climate-neutral district. In particular some key factors are interesting: - the presence of one of the largest photovoltaic parks in Europe on the roofs of CAAB, characterised by a production of 11,350,000 Kw/h of primary energy; - the presence of companies attentive to the issues of climate change and energy, able to act as facilitators for the area. This is the case of FIVE, a leader in the production of electric bicycles, whose plant is the first nZEB (nearly Zero Energy Building) productive building in the city; - the high presence of industrial buildings of different sizes needing a reduction in energy consumption; - the presence of obsolete, sometimes in decay, and of general highly energy-intensive buildings in the Pilastro area, accompanied by spread phenomena of energy poverty; - the presence of spaces that could be converted (e.g. unused warehouses, unexploited green areas, etc.); - the presence of an active community, characterised by numerous associations, but also by social challenges linked to multiple vulnerabilities; - the presence of local actors interested in the development of the area (including the Municipality, the University, Confindustria, ENEA, Confartigianato, etc.). Two main research projects are actually ongoing in the area, applying solutions towards energy improvement and transition strategies to guide the area towards climate neutrality: - GECO - Green Energy Community, funded by EIT Climate-KIC and active since 2019, aims to trigger a virtuous path of energy sharing between companies and citizens through the creation of an energy community. - GRETA - Green Energy Transition Actions, funded by the H2020 programme, aims to understand drivers and barriers on the involvement of citizens in the energy transition processes, by formulating Community Transition Pathways and Energy Citizenship Contracts. [from: Boeri, A., Boulanger, S., Turci, G., Pagliula, S. (2021) Strategie e tecnologie abilitanti per PED misti: efficienza tra smart cities e industria 4.0. TECHNE, 22, 180-190] | ||||||
| A1P025: Estimated PED case study / PED LAB costs | ||||||||
| A1P025: Estimated PED case study / PED LAB costs [mil. EUR] | 25 | 7804440 | ||||||
| Contact person for general enquiries | ||||||||
| A1P026: Name | Jasper Tonen, Elisabeth Koops | Jaanus Tamm | Tonje Healey Trulsrud | Prof. Danila Longo | Christoph Gollner | Abel Magyari | Christoph Gollner | Markus Paulsson |
| A1P027: Organization | Municipality of Groningen | Tartu City Government | Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) | University of Bologna - Architecture Department | FFG | ABUD | FFG | City of Lund |
| A1P028: Affiliation | Municipality / Public Bodies | Municipality / Public Bodies | Research Center / University | Research Center / University | Other | Research Center / University | Other | Municipality / Public Bodies |
| A1P028: Other | ||||||||
| A1P029: Email | Jasper.tonen@groningen.nl | Jaanus.tamm@tartu.ee | tonje.h.trulsrud@ntnu.no | christoph.gollner@ffg.at | magyari.abel@abud.hu | christoph.gollner@ffg.at | markus.paulsson@lund.se | |
| Contact person for other special topics | ||||||||
| A1P030: Name | Kaspar Alev | Strassl Ingeborg | Eva Dalman | |||||
| A1P031: Email | Kaspar.alev@tartu.ee | inge.strassl@salzburg.gv.at | eva.dalman@lund.se | |||||
| Pursuant to the General Data Protection Regulation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| A2P001: Fields of application | ||||||||
| A2P001: Fields of application |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| A2P001: Other | Walkability and biking | |||||||
| A2P002: Tools/strategies/methods applied for each of the above-selected fields | ||||||||
| A2P002: Tools/strategies/methods applied for each of the above-selected fields | Energy efficiency: - buildings energy retrofit supported by tax bonuses - replacing heat supply technologies Energy production: - installation of new (PV) systems for renewable on-site energy production; - presence of a large PV plant in the South East (2 solar parks: 12MW and 107MW) and North area (0,4 MW) Energy flexibility: - energy storage solutions, battery storage and possible hydrogen production - GRID balancing services E-mobility - Installation of new charging stations for electric vehicles; Urban Management - make use of the organizational structure Waste Management - circular use of municipal waste streams | Energy efficiency: - buildings retrofitting - combined public and private financing - low temperature central heating - LED lighting Energy production: - installation of photovoltaic (PV) systems for renewable on-site energy production; Digital technologies: - smart-meters smart home system. Smart city information platform E-mobility - Installation of new charging stations for electric vehicles; - e-bike/bikesharing services implementation. Urban comfort and air quality - Control units for air pollutants concentration (PM2.5, PM10, NO2) - Sustainable Energy and Climate Action Plan - SECAP) | Energy efficiency: Energy efficient envelope, with good insulation, triple glazing windows and airtight envelope. (EPC = 0) Energy Flexibility: MCP controls for the heat pump in the apartments. Energy production: PV panels on the roof, Ground source heat pumps Waste management: construction waste was kept to a minimum and sorted and collected separately as much as possible. Indoor air quality: Exhaust ventilation and opening of windows Construction materials: low carbon emission building materials | Energy efficiency: - buildings energy retrofit supported by tax incentives (110%, façade bonus, eco-bonus, sismabonus, renovation bonus, etc.); - several activities - such as Workshops, Webinars, Roundtables, Urban Trekking, etc…- are encouraged in the area to deepen knowledge and raise awareness on energy issues among urban stakeholders (householders, occupants, workers, etc..); - reduction in energy consumption also through every day energy saving actions. The spread of energy poverty phenomena in the area is considered urgent both for the medium-low-income population living in Pilastro and for small and medium-sized enterprises placed in Roveri; - Project for a One-stop-shop to guide residents and enterprises towards more conscious energy behaviours (planned in Bologna SECAP). Energy production: - installation of new photovoltaic (PV) systems for renewable on-site energy production; - presence of a waste to energy plant connected to the district heating system; - presence of a large PV plant in the CAAB area - 11,350,000 Kw/h Energy flexibility: - testing energy community and collective self-consumption feasibility in Pilastro area through an active citizens involvement process; - testing energy community feasibility among SMEs in Roveri industrial area; - testing the potential of complementary energy consumption profiles between residential area (Pilastro) and industrial area (Roveri). Digital technologies: - smart-meters installation in some dwellings in order to monitor consumption and suggest more sustainable energy behaviors; - Blog Pilastro as a tool to inform about the main activities and events ongoing in the area; E-mobility - Installation of new charging stations for electric vehicles; - e-bike/bikesharing services recovery (in fact during Covid-19 in the area Mobike service was suspended) and implementation. Urban comfort and air quality - Control units for air pollutants concentration (PM2.5, PM10, NO2); - Microclimatic simulation | - Dynamic district, and building scale energy modelling - Microclimate modelling - Klimaaktiv certification system - Energy community - Flexibility with shared heating and electricity systems | LundaMaTs methodology for traffic and city planning. LundaEko - Lund's programme for ecological sustainability. Municipally owned land is sold to property developers on environmental conditions. | ||
| A2P003: Application of ISO52000 | ||||||||
| A2P003: Application of ISO52000 | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | ||
| A2P004: Appliances included in the calculation of the energy balance | ||||||||
| A2P004: Appliances included in the calculation of the energy balance | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | ||
| A2P005: Mobility included in the calculation of the energy balance | ||||||||
| A2P005: Mobility included in the calculation of the energy balance | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | ||
| A2P006: Description of how mobility is included (or not included) in the calculation | ||||||||
| A2P006: Description of how mobility is included (or not included) in the calculation | Mobility, till now, is not included in the energy model. | not included | Today electrically charged vehicles are included in the energy balance. In the future also other fuels should be included. | |||||
| A2P007: Annual energy demand in buildings / Thermal demand | ||||||||
| A2P007: Annual energy demand in buildings / Thermal demand [GWh/annum] | 2.3 | 9.1 | 0.148 | 25 | ||||
| A2P008: Annual energy demand in buildings / Electric Demand | ||||||||
| A2P008: Annual energy demand in buildings / Electric Demand [GWh/annum] | 0.33 | 0.109 | 30 | |||||
| A2P009: Annual energy demand for e-mobility | ||||||||
| A2P009: Annual energy demand for e-mobility [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P010: Annual energy demand for urban infrastructure | ||||||||
| A2P010: Annual energy demand for urban infrastructure [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P011: Annual renewable electricity production on-site during target year | ||||||||
| A2P011: PV | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| A2P011: PV - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | 0.058 | 0.7770664 | ||||||
| A2P011: Wind | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P011: Wind - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P011: Hydro | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Hydro - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P011: Biomass_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Biomass_el - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P011: Biomass_peat_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Biomass_peat_el - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P011: PVT_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: PVT_el - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P011: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P011: Other - specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P012: Annual renewable thermal production on-site during target year | ||||||||
| A2P012: Geothermal | yes | no | yes | no | no | yes | no | no |
| A2P012 - Geothermal: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P012: Solar Thermal | yes | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Solar Thermal: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | 0.5 | |||||||
| A2P012: Biomass_heat | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Biomass_heat: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | 0.1 | |||||||
| A2P012: Waste heat+HP | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P012 - Waste heat+HP: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | 200 | |||||||
| A2P012: Biomass_peat_heat | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Biomass_peat_heat: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P012: PVT_th | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - PVT_th: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P012: Biomass_firewood_th | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Biomass_firewood_th: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P012: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P012 - Other: Please specify production in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P013: Renewable resources on-site - Additional notes | ||||||||
| A2P013: Renewable resources on-site - Additional notes | Geothermal heatpump systems, Waste heat from data centers | *Annual energy use below is presentedin primary energy consumption | ||||||
| A2P014: Annual energy use | ||||||||
| A2P014: Annual energy use [GWh/annum] | 0.194 | 0.819016 | ||||||
| A2P015: Annual energy delivered | ||||||||
| A2P015: Annual energy delivered [GWh/annum] | 0.0368 | |||||||
| A2P016: Annual non-renewable electricity production on-site during target year | ||||||||
| A2P016: Annual non-renewable electricity production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | -1 | 0 | ||||||
| A2P017: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year | ||||||||
| A2P017: Gas | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Gas: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P017: Coal | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Coal: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P017: Oil | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Oil: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P017: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P017 - Other: Annual non-renewable thermal production on-site during target year [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P018: Annual renewable electricity imports from outside the boundary during target year | ||||||||
| A2P018: PV | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P018 - PV: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P018: Wind | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P018 - Wind: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P018: Hydro | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P018 - Hydro: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P018: Biomass_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P018 - Biomass_el: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P018: Biomass_peat_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - Biomass_peat_el: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P018: PVT_el | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - PVT_el: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P018: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P018 - Other: specify production in GWh/annum if available [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: Annual renewable thermal imports from outside the boundary during target year | ||||||||
| A2P019: Geothermal | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Geothermal: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: Solar Thermal | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Solar Thermal: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: Biomass_heat | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Biomass_heat: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: Waste heat+HP | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Waste heat+HP: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: Biomass_peat_heat | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Biomass_peat_heat: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: PVT_th | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 PVT_th: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: Biomass_firewood_th | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Biomass_firewood_th: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P019: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P019 Other: Please specify imports in GWh/annum [GWh/annum] | ||||||||
| A2P020: Share of RES on-site / RES outside the boundary | ||||||||
| A2P020: Share of RES on-site / RES outside the boundary | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A2P021: GHG-balance calculated for the PED | ||||||||
| A2P021: GHG-balance calculated for the PED [tCO2/annum] | 980 | -0.00043 | ||||||
| A2P022: KPIs related to the PED case study / PED Lab | ||||||||
| A2P022: Safety & Security | Personal Safety | |||||||
| A2P022: Health | Healthy community | CO2) levels, Predicted Mean Vote,Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied, Temperature, Relative Humidity, Illuminance, Daylight factor, Sound pressure levels | ||||||
| A2P022: Education | ||||||||
| A2P022: Mobility | Sustainable mobility | Mode of transport; Access to public transport | Maximum 1/3 transport with car | |||||
| A2P022: Energy | NOn-renewable primary energy balance, renewable energy ratio, grid purchase factor, load cover factor/self-generation, supply cover factor/self-consumption, net energy/net power, peak delivered/peak expoted, total greenhouse gas emission | Non-renewable primary energy balance, Renewable energy ratio, Grid Purchase factor, Load cover factor/Self-generation, Supply cover factor/Self-consumption, Net energy/Net power, Peak delivered/exported power, Connection capacity credit, Total greenhouse gas emissions | Energy efficiency in buildings; Net energy need; Gross energy need; Total energy need | Local energy production 150% of energy need | ||||
| A2P022: Water | ||||||||
| A2P022: Economic development | capital costs, operational cots, overall economic performance (5 KPIs) | Investment costs, Share of investments covered by grants, Maintenance-related costs, Requirement-related costs, Operation-related costs, Other costs, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return, Economic Value Added, Payback Period, nZEB Cost Comparison | ||||||
| A2P022: Housing and Community | demographic composition, diverse community, social cohesion | Access to services, Affordability of energy, Affordability of housing, Democratic legitimacy, Living conditions, Social cohesion, Personal safety, Energy consciousness | Delivery and proximity to amenities | 50% rental apartments and 50% owner apartments | ||||
| A2P022: Waste | ||||||||
| A2P022: Other | Smartness and flecibility, Indoor Environmental Quality, Social performance - Equity (affordable housing, access to servicees and amenitioes, afforability of energy, living conditions, sustinable mobility, universal design) | GHG emissions; Power/load; Life cycle cost (LCC); Demographic needs and consultation plan; Public Space | ||||||
| A2P023: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Energy Generation | ||||||||
| A2P023: Photovoltaics | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| A2P023: Solar thermal collectors | yes | no | no | yes | yes | no | yes | yes |
| A2P023: Wind Turbines | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P023: Geothermal energy system | yes | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| A2P023: Waste heat recovery | yes | no | no | no | no | no | yes | yes |
| A2P023: Waste to energy | yes | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Polygeneration | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P023: Co-generation | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Heat Pump | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | yes | yes |
| A2P023: Hydrogen | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P023: Hydropower plant | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Biomass | no | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Biogas | no | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P023: Other | Wave | |||||||
| A2P024: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Energy Flexibility | ||||||||
| A2P024: A2P024: Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) | yes | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: Energy management system | yes | yes | yes | no | no | yes | no | yes |
| A2P024: Demand-side management | yes | no | yes | no | no | yes | no | yes |
| A2P024: Smart electricity grid | no | no | no | no | yes | yes | no | yes |
| A2P024: Thermal Storage | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: Electric Storage | yes | no | no | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: District Heating and Cooling | yes | yes | no | yes | no | no | yes | yes |
| A2P024: Smart metering and demand-responsive control systems | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P024: P2P – buildings | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no | no |
| A2P024: Other | ||||||||
| A2P025: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Energy Efficiency | ||||||||
| A2P025: Deep Retrofitting | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Energy efficiency measures in historic buildings | yes | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: High-performance new buildings | yes | no | yes | yes | no | yes | no | yes |
| A2P025: Smart Public infrastructure (e.g. smart lighting) | yes | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P025: Urban data platforms | yes | yes | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P025: Mobile applications for citizens | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Building services (HVAC & Lighting) | no | no | yes | yes | no | yes | no | yes |
| A2P025: Smart irrigation | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Digital tracking for waste disposal | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P025: Smart surveillance | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| A2P025: Other | ||||||||
| A2P026: Technological Solutions / Innovations - Mobility | ||||||||
| A2P026: Efficiency of vehicles (public and/or private) | no | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| A2P026: Measures to reduce traffic volume (e.g. measure to support public transportation, shared mobility, measure to reduce journeys and distances) | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes |
| A2P026: e-Mobility | yes | yes | no | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| A2P026: Soft mobility infrastructures and last mile solutions | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P026: Car-free area | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| A2P026: Other | ||||||||
| A2P027: Mobility strategies - Additional notes | ||||||||
| A2P027: Mobility strategies - Additional notes | Shared mobility: a mobility point will be implemented and ensure the flexible use of different mobility services. | Walkability | ||||||
| A2P028: Energy efficiency certificates | ||||||||
| A2P028: Energy efficiency certificates | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| A2P028: If yes, please specify and/or enter notes | Energy Performance Certificate | EPC = 0, energy neutral building | Energy Performance Certificate for each dwelling | Energy Performance Certificate | Miljöbyggnad silver/guld | |||
| A2P029: Any other building / district certificates | ||||||||
| A2P029: Any other building / district certificates | No | No | Yes | No | ||||
| A2P029: If yes, please specify and/or enter notes | Klimaaktiv certificate, Greenpass certificate | |||||||
| A3P001: Relevant city /national strategy | ||||||||
| A3P001: Relevant city /national strategy |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| A3P002: Quantitative targets included in the city / national strategy | ||||||||
| A3P002: Quantitative targets included in the city / national strategy | City level targets Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (PUMS) - 2019 | Targets: - by 2030 440,000 daily trips will no longer be made by car but on foot, by bike or by public transport; - by 2030 12% of vehicles will be electric; Sustainable Energy and Climate Action Plan (SECAP) - 2021 | Targets: - by 2025 deep renovation of 3% per year of residential homes (insulation of building envelopes and adoption of heat pump heating system); - by 2030 reduction of electricity consumption at least of 20% compared to 2018; - by 2030 100% coverage of electricity consumption for municipal buildings; - by 2030 increase public green areas by at least 10% Urban General Plan (PUG) - 2021 | Targets: - by 2030 net zero land consumption; National level targets Integrated National Energy and Climate Plan - 2020 | Targets: - by 2030 reduction of 43% for primary energy consumption, with respect to the reference 2007 scenario. - by 2030 increase of 30% of energy production from renewable sources; - by 2025 energy generation for electricity independent from the use of coal; | City strategy: Net climate neutrality 2030 | ||||||
| A3P003: Strategies towards decarbonization of the gas grid | ||||||||
| A3P003: Strategies towards decarbonization of the gas grid |
|
|
|
| ||||
| A3P003: Other | No gas grid in Brunnshög | |||||||
| A3P004: Identification of needs and priorities | ||||||||
| A3P004: Identification of needs and priorities | Bologna needs to reach the climate neutrality proceeding by ‘part’ of the city. Pilastro-Roveri is a promising district due to the following reasons: - some buildings need to be renovated both to increase the energy performance, the seismic behaviour, spaces liveability and comfort; - Pilastro is a residential area with the presence of a high percentage of vulnerable inhabitants affected by energy poverty phenomenon. This situation needs to be prioritized; - Pilastro is characterized by the presence of large underused green spaces that can represent a valuable resource for social cohesion and for heat island phenomenon mitigation; - Roveri is an industrial area where some small-medium enterprises are investing in order to improve their facilities and to efficiency their production cycle; - Roveri and Pilastro areas present complementary energy consumption curves throughout the day/week with a high potential for energy sharing and flexibility. | Local waste heat is utlized to a very large extent. More local electricity production is needed. Need to minimise the use of private cars. | ||||||
| A3P005: Sustainable behaviour | ||||||||
| A3P005: Sustainable behaviour | In Groningen we are working with different sustainable behaviours approaches and also developed the Unified Citizen Engagement Approach (UCEA). Currently, there are two different approaches in use in the municipality of Groningen: the District energy approach (Wijkgerichte aanpak, developed by the Municipality of Groningen) and the Cooperative approach (Coöperative Aanpak, developed by Grunneger Power). Based upon those approaches and knowledge that is gained through social research executed by TNO and HUAS the new Unified Citizen Engagement Approach (UCEA) has been developed. | Bologna SECAP, as well as the participation to the 100 Climate-Neutral Cities, promotes the PED model as an enabling tool to foster city energy transition process. In Pilastro-Roveri district two main sustainable behaviours approaches can be identified: - bottom-up approach - some citizens are joining forces to create groups of energy self-consumption, in view of energy communities’ implementation and, at the same time, some companies have already undertaken some efficiency intervention on the production system by leveraging highly energy-efficient technologies; - top-down approach - GECO and GRETA are international ongoing projects on the area that promote innovation and energy transition with important fundings from the European Union, but with a particular focus on citizen engagement and participatory approach. Simultaneously, new and updated planning tools such as PUG, SECAP and SUMP identify in this part of Bologna city a key area to enable an ecological transition process holding together all relevant stakeholders - citizens, small-medium enterprises and Institutions. These two thrusts (bottom-up and top-down) need to be optimized in view of a participatory pathway towards the grounding of a Positive Energy District in Pilastro-Roveri. | Need to minimise the use of private cars. Need to provide efficient methods for sorce separated waste collection. | |||||
| A3P006: Economic strategies | ||||||||
| A3P006: Economic strategies |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| A3P006: Other | Attractivenes | |||||||
| A3P007: Social models | ||||||||
| A3P007: Social models |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| A3P007: Other | ||||||||
| A3P008: Integrated urban strategies | ||||||||
| A3P008: Integrated urban strategies |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| A3P008: Other | ||||||||
| A3P009: Environmental strategies | ||||||||
| A3P009: Environmental strategies |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| A3P009: Other | ||||||||
| A3P010: Legal / Regulatory aspects | ||||||||
| A3P010: Legal / Regulatory aspects | At national/regional/local level a legislation on PEDs development is not yet available in the Netherlands. There will be a new Environmental Act and Heat Act in the nearby future. We are working on a paper about the current legal barriers, which are in short for Groningen: Lack of legal certainty and clarity with regard to the energy legislation. Lack of coherence between policy and legislation from different ministries. The planned revision of the Dutch Heat Law prevents Groningen from effectively realizing sustainable heat transition plans and goals. Lack of capacity on the distribution grid for electricity | PEDs in Italy are meant as strategies towards climate-neutrality: at national/regional/local level a specific legislation on PEDs development is not yet available. However, the European Commission has legislated on Energy Community (‘Renewable energy’ directive - 2018/2001/EU and ‘Common rules for the internal electricity market’ directive- 2019/944/EU). Italy, starting from 2020, has transposed the Directives at national level (‘Milleproroghe’ decree then made effective by ‘Promotion of Renewable sources’ decree 199/2021). At regional level Emilia Romagna in May 2022 developed a law encouraging EC model diffusion (LR 5/2022 ‘Promotion and support of renewable energy communities and renewable energy self-consumers acting collectively’). Energy Community, according to Lindholm et al. 2021, can be considered as ‘a first implementation step towards PEDs.’ | The municipality cannot demand a specific energy solution to private property owners. It has to be voluntary and market based solutions. | |||||
| B1P001: PED/PED relevant concept definition | ||||||||
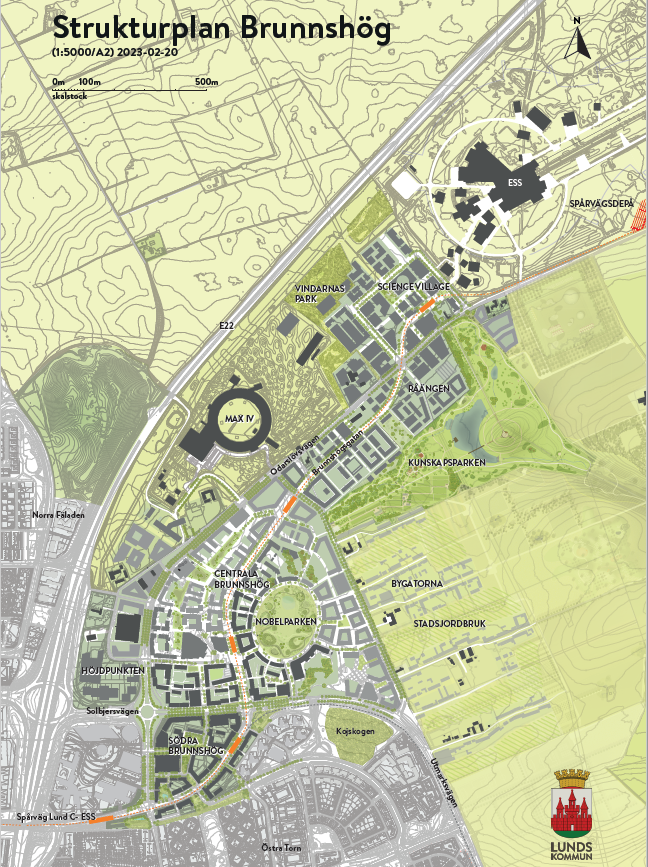
| B1P001: PED/PED relevant concept definition | The demonstration projects is a new residential development, which consists of an apartment complex which includes 39 apartments spread over 3 floors. It is a sustainble plus energy neighbouhood, and has reached a plus energy balance on its first year in operation. It has MPC controls on the individual heat pumps to improve the energy flexibility of the apartments. It includes the "social beatiful" concepts with a strong emphasis on the social sustainability of the project. | Pilastro-Roveri district can be considered as a PED-relevant area. Even though at the moment the area doesn’t meet annual energy positive balance, it addresses some relevant key aspects listed in the JPI UE PED Framework Definition such as: - high level of aspiration in terms of energy efficiency, energy flexibility and energy production; - integration of different systems and infrastructures; - inclusion of aspects not only related to energy sector, but also connected with social, economic and environmental sustainability. | Vision: The city as a power plant. The ultimate goal is that more energy is produced within the distric boundaries than is being used (heating, electricity & mobility). Energy efficient buildings, efficient mobility, reuse of residual heat and solar electricity are the main methods. | |||||
| B1P002: Motivation behind PED/PED relevant project development | ||||||||
| B1P002: Motivation behind PED/PED relevant project development | The need for social housing and the ambition to create a great living environment with a high-performance apartment complex, supplied with renewable energy. It results in lower energy bills for the tenants and high-quality homes. | Pilastro-Roveri district is not actually meant to become a PEDs. However, it can be considered as a PED-relevant case-study since a participatory transition pathway towards a more sustainable, efficient and resilient district is gaining ground, involving the main urban stakeholders. At the same time, the most recent city plan and policies (such as the city SECAPs - updated in 2021) are promoting PED model as a key strategy to guide Bologna towards climate neutrality by 2030. | The aim is to build a sustainable city with minimal climate impact and maximum quality of life. PED is an important step to acheive the aims of a very ambitious city development. | |||||
| B1P003: Environment of the case study area | ||||||||
| B2P003: Environment of the case study area | Urban area | Suburban area | Urban area | Suburban area | Suburban area | Suburban area | Urban area | |
| B1P004: Type of district | ||||||||
| B2P004: Type of district |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| B1P005: Case Study Context | ||||||||
| B1P005: Case Study Context |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| B1P006: Year of construction | ||||||||
| B1P006: Year of construction | 2024 | |||||||
| B1P007: District population before intervention - Residential | ||||||||
| B1P007: District population before intervention - Residential | 4500 | 0 | ||||||
| B1P008: District population after intervention - Residential | ||||||||
| B1P008: District population after intervention - Residential | 18000 | |||||||
| B1P009: District population before intervention - Non-residential | ||||||||
| B1P009: District population before intervention - Non-residential | 2000 | |||||||
| B1P010: District population after intervention - Non-residential | ||||||||
| B1P010: District population after intervention - Non-residential | 22000 | |||||||
| B1P011: Population density before intervention | ||||||||
| B1P011: Population density before intervention | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B1P012: Population density after intervention | ||||||||
| B1P012: Population density after intervention | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.026666666666667 |
| B1P013: Building and Land Use before intervention | ||||||||
| B1P013: Residential | no | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Residential: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P013: Office | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| B1P013 - Office: Specify the sqm [m²] | 60000 | |||||||
| B1P013: Industry and Utility | no | no | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Industry and Utility: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P013: Commercial | no | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Commercial: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P013: Institutional | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Institutional: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P013: Natural areas | no | yes | no | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| B1P013 - Natural areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | 2000000 | |||||||
| B1P013: Recreational | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Recreational: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P013: Dismissed areas | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| B1P013 - Dismissed areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P013: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| B1P013 - Other: Specify the sqm [m²] | Outdoor parking: 100000 | |||||||
| B1P014: Building and Land Use after intervention | ||||||||
| B1P014: Residential | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| B1P014 - Residential: Specify the sqm [m²] | 2394 | 600000 | ||||||
| B1P014: Office | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| B1P014 - Office: Specify the sqm [m²] | 650000 | |||||||
| B1P014: Industry and Utility | no | no | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Industry and Utility: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P014: Commercial | no | yes | no | yes | yes | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Commercial: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P014: Institutional | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| B1P014 - Institutional: Specify the sqm [m²] | 50000 | |||||||
| B1P014: Natural areas | no | yes | no | yes | yes | yes | no | no |
| B1P014 - Natural areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P014: Recreational | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| B1P014 - Recreational: Specify the sqm [m²] | 400000 | |||||||
| B1P014: Dismissed areas | no | no | no | yes | no | no | no | no |
| B1P014 - Dismissed areas: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B1P014: Other | no | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no |
| B1P014 - Other: Specify the sqm [m²] | ||||||||
| B2P001: PED Lab concept definition | ||||||||
| B2P001: PED Lab concept definition | Groningen was selected as Lighthouse City for the MAKING-CITY project. MAKING-CITY is a 60-month Horizon 2020 project launched in December 2018. It aims to address and demonstrate the urban energy system transformation towards smart and low-carbon cities, based on the Positive Energy District (PED) concept. The PED operational models developed in MAKING-CITY will help European and other cities around the world to adopt a long-term City Vision 2050 for energy transition and sustainable urbanisation whilst turning citizens into actors of this transformation. Groningen works with two PED districts in two completely different neighbourhoods in terms of structure and buildings. This is why we see this as a lab: to see wat works and what doesn’t. In order to be able to implement this in the rest of the city. | |||||||
| B2P002: Installation life time | ||||||||
| B2P002: Installation life time | The MAKING-CITY project lasts from November 2018 – November 2023. By that time PED North and PED South East are a fact. | |||||||
| B2P003: Scale of action | ||||||||
| B2P003: Scale | District | District | City | |||||
| B2P004: Operator of the installation | ||||||||
| B2P004: Operator of the installation | The Municipality of Groningen is Manager of the lab but works closely with other parties such as the university, university of applied sciences, research institute TNO and several other parties. | |||||||
| B2P005: Replication framework: Applied strategy to reuse and recycling the materials | ||||||||
| B2P005: Replication framework: Applied strategy to reuse and recycling the materials | Groningen does not have a strategy to reuse and recyle materials | |||||||
| B2P006: Circular Economy Approach | ||||||||
| B2P006: Do you apply any strategy to reuse and recycling the materials? | No | No | ||||||
| B2P006: Other | ||||||||
| B2P007: Motivation for developing the PED Lab | ||||||||
| B2P007: Motivation for developing the PED Lab |
|
| ||||||
| B2P007: Other | ||||||||
| B2P008: Lead partner that manages the PED Lab | ||||||||
| B2P008: Lead partner that manages the PED Lab | Municipality | Municipality | ||||||
| B2P008: Other | ||||||||
| B2P009: Collaborative partners that participate in the PED Lab | ||||||||
| B2P009: Collaborative partners that participate in the PED Lab |
|
| ||||||
| B2P009: Other | research companies, monitoring company, ict company | |||||||
| B2P010: Synergies between the fields of activities | ||||||||
| B2P010: Synergies between the fields of activities | ||||||||
| B2P011: Available facilities to test urban configurations in PED Lab | ||||||||
| B2P011: Available facilities to test urban configurations in PED Lab |
|
| ||||||
| B2P011: Other | ||||||||
| B2P012: Incubation capacities of PED Lab | ||||||||
| B2P012: Incubation capacities of PED Lab |
|
| ||||||
| B2P013: Availability of the facilities for external people | ||||||||
| B2P013: Availability of the facilities for external people | ||||||||
| B2P014: Monitoring measures | ||||||||
| B2P014: Monitoring measures |
|
| ||||||
| B2P015: Key Performance indicators | ||||||||
| B2P015: Key Performance indicators |
|
| ||||||
| B2P016: Execution of operations | ||||||||
| B2P016: Execution of operations | ||||||||
| B2P017: Capacities | ||||||||
| B2P017: Capacities | ||||||||
| B2P018: Relations with stakeholders | ||||||||
| B2P018: Relations with stakeholders | ||||||||
| B2P019: Available tools | ||||||||
| B2P019: Available tools |
|
| ||||||
| B2P019: Available tools | ||||||||
| B2P020: External accessibility | ||||||||
| B2P020: External accessibility | ||||||||
| C1P001: Unlocking Factors | ||||||||
| C1P001: Recent technological improvements for on-site RES production | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P001: Innovative, integrated, prefabricated packages for buildings envelope / Energy efficiency of building stock | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P001: Energy Communities, P2P, Prosumers concepts | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P001: Storage systems and E-mobility market penetration | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P001: Decreasing costs of innovative materials | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Financial mechanisms to reduce costs and maximize benefits | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P001: The ability to predict Multiple Benefits | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P001: The ability to predict the distribution of benefits and impacts | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P001: Citizens improved awareness and engagement on sustainable energy issues (bottom-up) | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P001: Social acceptance (top-down) | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P001: Improved local and national policy frameworks (i.e. incentives, laws etc.) | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P001: Presence of integrated urban strategies and plans | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P001: Multidisciplinary approaches available for systemic integration | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P001: Availability of grants (from EC or other donors) to finance the PED Lab projects | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P001: Availability of RES on site (Local RES) | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P001: Ongoing or established collaboration on Public Private Partnership among key stakeholders | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P001: Any other UNLOCKING FACTORS | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P001: Any other UNLOCKING FACTORS (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P002: Driving Factors | ||||||||
| C1P002: Climate Change adaptation need | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P002: Climate Change mitigation need (local RES production and efficiency) | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P002: Rapid urbanization trend and need of urban expansions | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P002: Urban re-development of existing built environment | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P002: Economic growth need | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P002: Improved local environmental quality (air, noise, aesthetics, etc.) | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P002: Territorial and market attractiveness | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P002: Energy autonomy/independence | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P002: Any other DRIVING FACTOR | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P002: Any other DRIVING FACTOR (if any) | Earthquakes due to gas extraction | |||||||
| C1P003: Administrative barriers | ||||||||
| C1P003: Difficulty in the coordination of high number of partners and authorities | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P003: Lack of good cooperation and acceptance among partners | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P003: Lack of public participation | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P003: Lack of institutions/mechanisms to disseminate information | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P003:Long and complex procedures for authorization of project activities | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P003: Time consuming requirements by EC or other donors concerning reporting and accountancy | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P003: Complicated and non-comprehensive public procurement | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P003: Fragmented and or complex ownership structure | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P003: City administration & cross-sectoral attitude/approaches (silos) | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P003: Lack of internal capacities to support energy transition | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P003: Any other Administrative BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P003: Any other Administrative BARRIER (if any) | Delay in the Environmental Dialogue processing in the municipality | |||||||
| C1P004: Policy barriers | ||||||||
| C1P004: Lack of long-term and consistent energy plans and policies | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P004: Lacking or fragmented local political commitment and support on the long term | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P004: Lack of Cooperation & support between national-regional-local entities | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P004: Any other Political BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P004: Any other Political BARRIER (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P005: Legal and Regulatory barriers | ||||||||
| C1P005: Inadequate regulations for new technologies | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P005: Regulatory instability | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P005: Non-effective regulations | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P005: Unfavorable local regulations for innovative technologies | 3 - Moderately important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P005: Building code and land-use planning hindering innovative technologies | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P005: Insufficient or insecure financial incentives | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P005: Unresolved privacy concerns and limiting nature of privacy protection regulation | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P005: Shortage of proven and tested solutions and examples | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P005: Any other Legal and Regulatory BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P005: Any other Legal and Regulatory BARRIER (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P006: Environmental barriers | ||||||||
| C1P006: Environmental barriers | ? | |||||||
| C1P007: Technical barriers | ||||||||
| C1P007: Lack of skilled and trained personnel | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P007: Deficient planning | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P007: Retrofitting work in dwellings in occupied state | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P007: Lack of well-defined process | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Inaccuracy in energy modelling and simulation | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P007: Lack/cost of computational scalability | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P007: Grid congestion, grid instability | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P007: Negative effects of project intervention on the natural environment | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P007: Energy retrofitting work in dense and/or historical urban environment | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P007: Difficult definition of system boundaries | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P007: Any other Thecnical BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P007: Any other Thecnical BARRIER (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P008: Social and Cultural barriers | ||||||||
| C1P008: Inertia | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Lack of values and interest in energy optimization measurements | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P008: Low acceptance of new projects and technologies | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P008: Difficulty of finding and engaging relevant actors | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P008: Lack of trust beyond social network | 4 - Important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Rebound effect | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P008: Hostile or passive attitude towards environmentalism | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P008: Exclusion of socially disadvantaged groups | 5 - Very important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P008: Non-energy issues are more important and urgent for actors | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Hostile or passive attitude towards energy collaboration | 2 - Slightly important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P008: Any other Social BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P008: Any other Social BARRIER (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P009: Information and Awareness barriers | ||||||||
| C1P009: Insufficient information on the part of potential users and consumers | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P009: Perception of interventions as complicated and expensive, with negative socio-economic or environmental impacts | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P009: Lack of awareness among authorities | 2 - Slightly important | 2 - Slightly important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P009: Information asymmetry causing power asymmetry of established actors | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P009: High costs of design, material, construction, and installation | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P009: Any other Information and Awareness BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P009: Any other Information and Awareness BARRIER (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P010: Financial barriers | ||||||||
| C1P010: Hidden costs | 2 - Slightly important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P010: Insufficient external financial support and funding for project activities | 3 - Moderately important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P010: Economic crisis | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P010: Risk and uncertainty | 3 - Moderately important | 4 - Important | 5 - Very important | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P010: Lack of consolidated and tested business models | 3 - Moderately important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important |
| C1P010: Limited access to capital and cost disincentives | 2 - Slightly important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important |
| C1P010: Any other Financial BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P010: Any other Financial BARRIER (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P011: Market barriers | ||||||||
| C1P011: Split incentives | 5 - Very important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P011: Energy price distortion | 4 - Important | 3 - Moderately important | 1 - Unimportant | 5 - Very important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 3 - Moderately important |
| C1P011: Energy market concentration, gatekeeper actors (DSOs) | 4 - Important | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 4 - Important | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 2 - Slightly important |
| C1P011: Any other Market BARRIER | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant | 1 - Unimportant |
| C1P011: Any other Market BARRIER (if any) | ||||||||
| C1P012: Stakeholders involved | ||||||||
| C1P012: Government/Public Authorities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| C1P012: Research & Innovation |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: Financial/Funding |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: Analyst, ICT and Big Data |
|
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Business process management |
|
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Urban Services providers |
|
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Real Estate developers |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: Design/Construction companies |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| C1P012: End‐users/Occupants/Energy Citizens |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| C1P012: Social/Civil Society/NGOs |
|
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Industry/SME/eCommerce |
|
|
|
| ||||
| C1P012: Other | ||||||||
| C1P012: Other (if any) | ||||||||
| Summary |

Authors (framework concept)
Beril Alpagut (Demir Energy); Giulia Turci (University of Bologna); Michal Kuzmic (Czech Technical University in Prague); Paolo Civiero (Università Roma Tre); Serena Pagliulia (University of Bologna); Oscar Seco (CIEMAT); Silvia Soutullo (CIEMAT); Daniele Vettorato (EURAC Research, IEA Annex 83); Bailador Ferreras M. Almudena (CIEMAT); Vicky Albert-Seifried (FHG ISE)
Contributors (to the content)
Laura Aelenei (LNEG), Nienke Maas (TNO), Savis Gohari (OsloMet), Andras Reith (ABUD), Ghazal Etminan (AIT), Maria-Beatrice Andreucci (Universita Sapienza), Francesco Reda (VTT, IEA Annex 83), Mari Hukkalainen (VTT), Judith-Borsboom (Locality), Gilda Massa (ENEA), Jelena Ziemele (University of Latvia), Nikola Pokorny (CVUT), Sergio Diaz de Garayo Balsategui (CENER, IEA Annex 83), Matthias Haaze (ZHAW, IEA Annex 83), Christoph Gollner (FFG, JPI UE), Silvia Bossi (ENEA, JPI UE), Christian Winzer (Zurich University of Applied Science), George Martinopoulos (Centre for Research and Technology Hellas), Maria Nuria Sánchez (CIEMAT), Angelina Tomova (Energy Agency of Plovdiv)
Implemented by
Boutik.pt: Filipe Martins, Jamal Khan
Marek Suchánek (Czech Technical University in Prague)